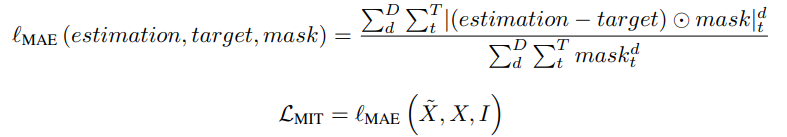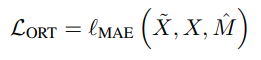SAITS: Self Attention-based Imputation for time series
The following contents are based on the paper “SAITS: Self Attention-based Imputation for Time Series” (Du, W., 2022)
self-attention-based mechanism은 compounding error에 덜 취약한 non-autoregressive 방식이고, slow speed와 memory constraints의 단점을 가진 recurrent neural network based 방식과는 다르게 weighted combination of two diagonally-masked self attention blocks (DMSA blocks)를 통해 temporal dependencies와 feature correlation between time steps를 capture한다. SAITS는 imputation과 reconstruction의 joint-optimization training approach를 활용한다.
What is self-attention
Self-attention은 주로 Natural Language Processing을 목적으로 활용되었다가 지금은 다양한 범위의 sequence modeling에 활용되는 기법이다. Self-attention module은 n개의 inputs를 사용해서 n개의 output을 반환하는데, input들이 서로 interact해서 input 자신(self)에 포함된 것들 중 어떤 것에 더 비중(attention)을 두어야할지를 찾는다. Self-attention mechanism의 output은 이런 interaction과 attention score의 aggregate이다.
2개의 input들이 주어진 self-attention module에서 수행되는 step들은 다음과 같다:
- prepare inputs(초록색)
- initialize wieghts
- derive key(주황색), query(빨간색), and value(보라색)
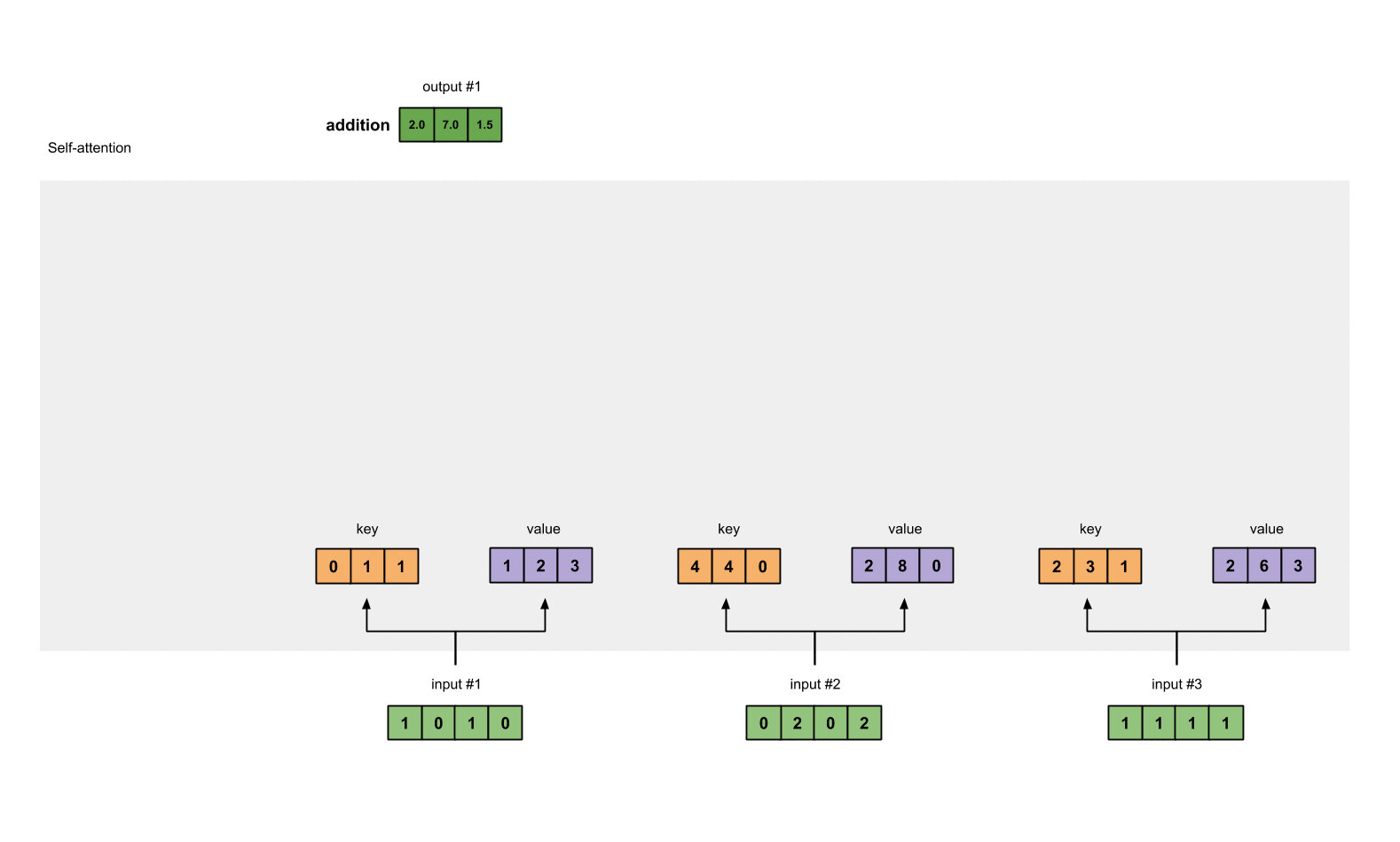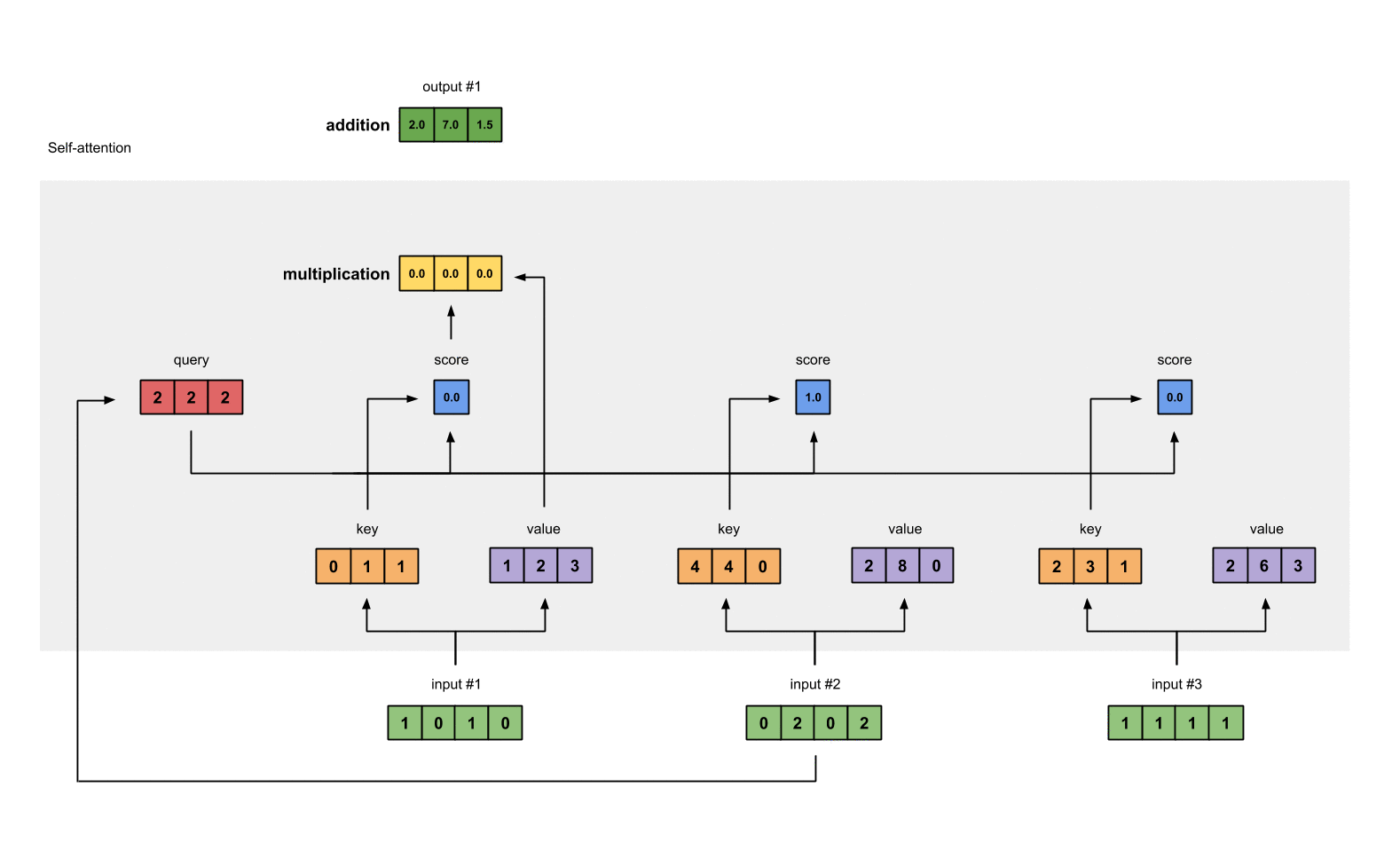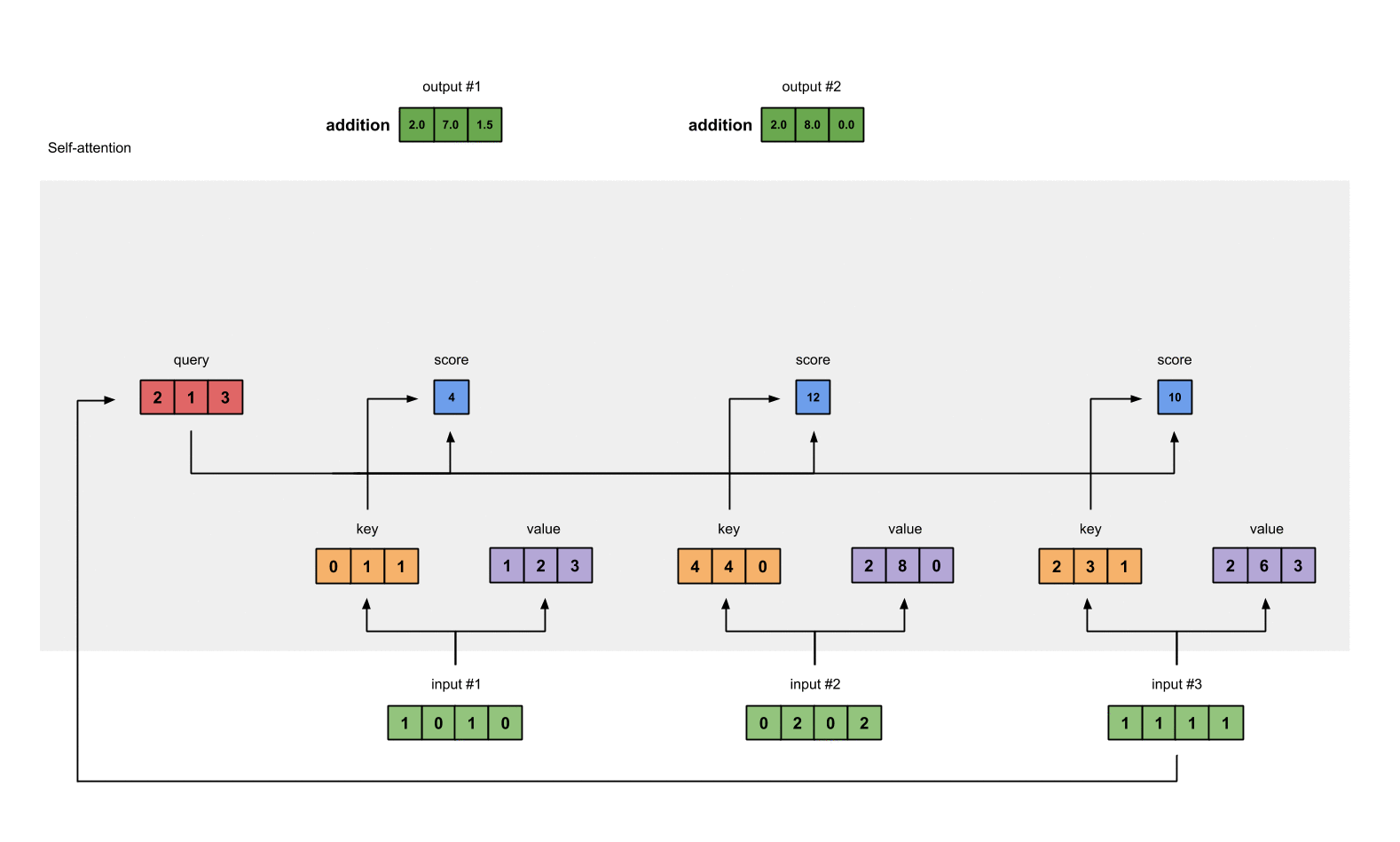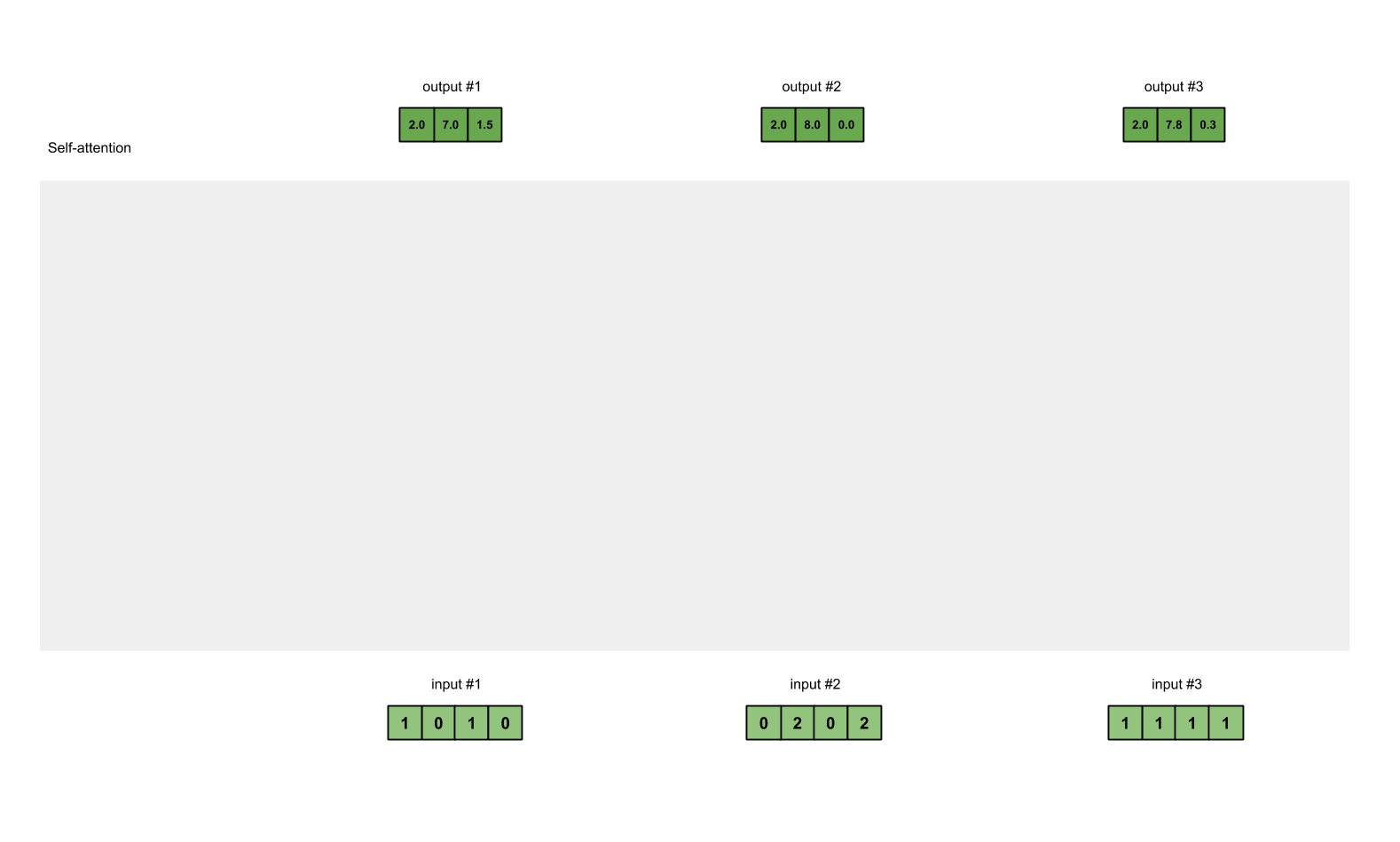
- calculate attention scores(파란색) for Input1
- calculate softmax of the scores
- multiply scores with values (노란색)
- sum weighted values to get Output1(초록색)
- Repeat steps4~7 for Input2 & Input3
SAITS overview
SAITS is composed of 2 learning tasks:
- MIT(Masked Imputation Task) - finds “imputation loss 부분”
- ORT(Observed Reconstruction Task) - finds “reconstruction loss 부분”
이 두 task 각각의 loss를 합쳐서 training loss를 계산하고 learning이 진행된다.
일반적으로 how a RNN model is trained for imputation (ORT task에 해당하는 부분만 구현된다):
- Input time series feature vectors X together with missing mask M (missing mask vector M consists of elements that is 1 if data is observed, 0 if data is missing). Alerts the model that input data has observations and missing values
- Let the model reconstruct the observed part of the input time series and calculate the reconstruction error in each time step –> “reconstruction loss”
- Utilize the reconstruction loss to update the model
위 방식과는 다르게 SAITS는 missing part 대비 observed part를 인지하여 ORT 기반의 training을 통해 reconstruction error를 최소화하는데에만 focus하지 않고, MIT task를 통해서 missing value들이 accurately impute되는지에도 focus한다(minimizing imputation error).
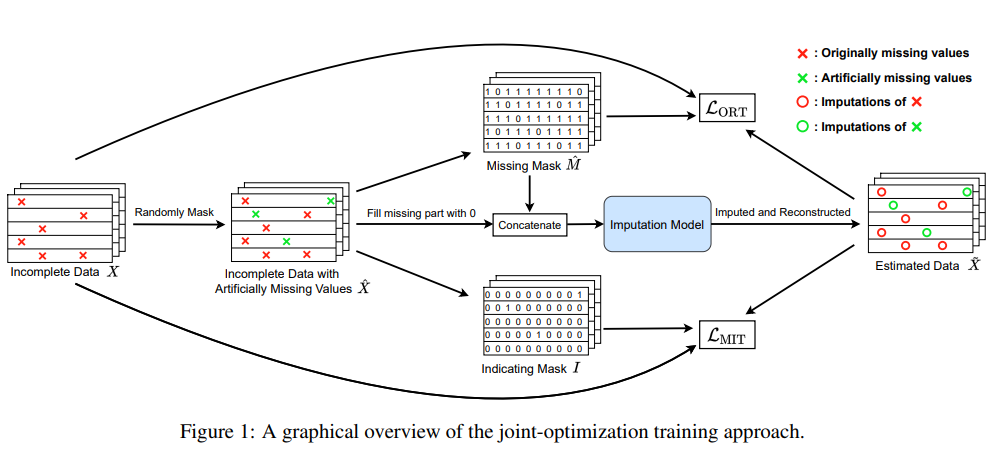
SAITS overview (shows how joint-optimization approach works)
MIT(Masked Imputation Task)
Artificially masked values를 기반으로 prediction task를 수행한다. For every batch input into the model, some % of observed values gets artificially masked at random. 원래 originally missing values로 부터 artificially masked values를 distinguish하기 위해 “indicating mask vector I”를 정의한다. vector I의 element는 1 if data is artificially masked, 0 otherwise. M_hat은 artificially masking된 후의 missing mask vector이다. 그래서 M_hat vector의 element들은 artificially + originally masked의 경우 0, otherwise 1이다.
MIT task로 부터 다음과 같이 MAE와 MIT loss를 계산한다.
ORT(Observed Reconstruction Task)
ORT는 위 RNN기반 방식에서 언급된바와 같이 observed values를 기반으로 한 reconstruction task이다. After model processing, observed values in the output are different from their original values, and they are called reconstruction. ORT loss는 다음과 같이 계산된다.
SAITS 방식에서는 MIT and ORT are integral.
MIT의 영향 - forces model to predict missing values accurately
ORT의 영향 - ensure model converges to the distribution of observed data
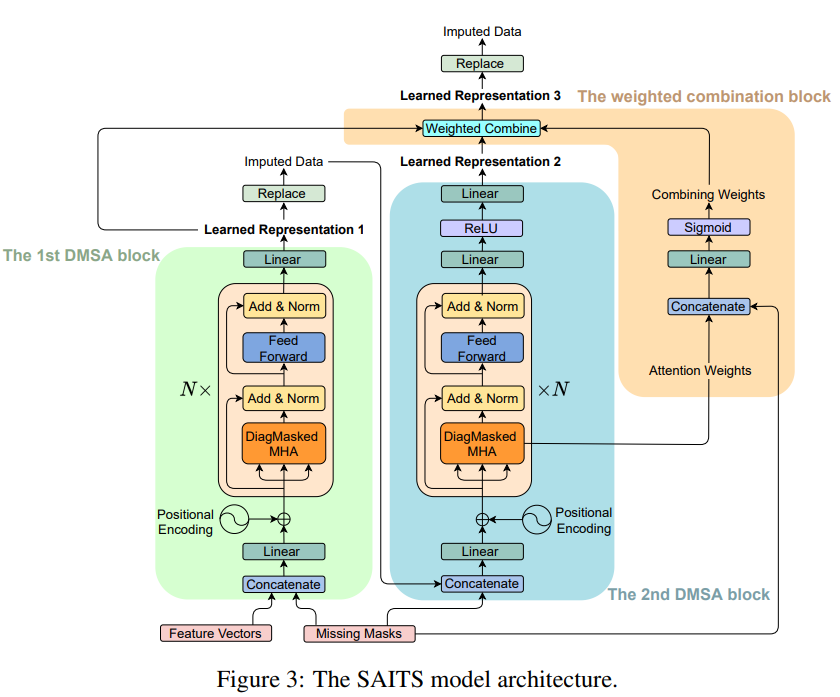
SAITS architecture
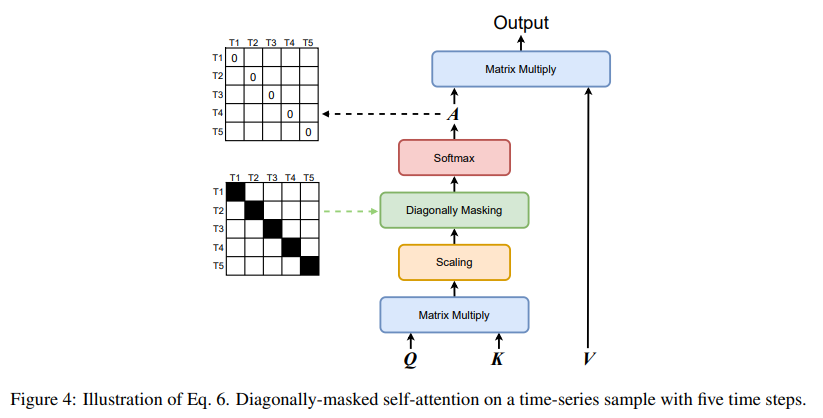
DMSA(Diagonally Masked Self Attention)
To enhance SAITS’ imputation ability, the diagonal masks are applied inside the self-attention. Diagonal mask를 사용하면, t-th step에서의 input value들은 자신들을 볼 수 없고 자신의 estimation에는 기여할 수 없다. (아래 그림 참조) 그래서 그들의 estimation은 other (T-1) time steps의 input values에 의존하게 된다. 이런 특징은 DMSA가 하나의 attention operation만으로도 temporal dependencies와 feature correlation (between time steps in high dimensional space)을 capture할 수 있게해준다.
References
- “Illustrated Self Attention” https://medium.com/towards-data-science/illustrated-self-attention-2d627e33b20a
- “SAITS: SELF-ATTENTION-BASED IMPUTATION FOR TIME SERIES” (Du, 2022)
- Wenjie Du. (2022). PyPOTS: A Python Toolbox for Data Mining on Partially-Observed Time Series. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6823222