A Survey of Methods for Encrypted Traffic Classification and Analysis (Velan, 2014)
this paper’s contribution
주요 encryption protocol과 이들의 packet structure 및 packet이 network에서 기본적으로 behave하는 방식을 설명한다. encrypted traffic classification/identification에서 주로 specific packet structure과 communication pattern을 사용하기 때문에 매우 중요함.
describe mostly widely usesd encryption protocols to show their packet structure and standard behavior in a network - forms the basis of all classification protocols which use either specific packet structure or communication pattern to identify encryption protocols.
investigate information provided by the encryption protocols (addressed above). Most protocols negotiate encryption algorithms in clear text, these data can be monitored (e.g., reveal the use of weak ciphers)
describe how the structure of encryption protocols can be used to detect these protocols in a network. there are traffic classification algorithms using such info & open-source tools that implement these algorithms.
extensive survey of behaviour-based methods for encypted traffic classification
대부분의 statistical and machine learning algorithm기반의 traffic classification은 SSH, SSL/TLS and encrypted BitTorrent와 같은 encryption protocols를 target 한다.
Encrypted protocols
encypted traffic classification 분야의 연구에서 주로 사용되는 encryption protocol로는
- IPsec,
- TLS,
- SSH,
- BitTorrent,
- Skype protocol이 있다.
ISO/OSI reference model에서 present된 protocols의 순서는 다음과 같다:
- IPsec protocol suite (operates on the network layer)
- TLS and SSH protocols (on the presentation layer)
- BitBorrent & Skype protocols (represent application layer, implementing their own protocols for secure transmission)
These protocols offer authentication of communication peers, data integrity, replay protection and non-repudiation
기본 OSI model

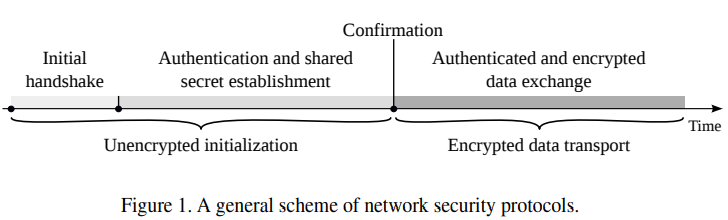
Common two main phases
모든 encryption protocols commonly have two main phases. 다음 그림과 같은 구성은 (with small modification) 거의 모든 protocols에 적용 가능하다.:
- initialization of the connection(unencrypted) - algorithm capabilities are usually exchanged, communication parties are authenticated and secret keys are established. authenticate된 secret key를 사용해서 다음 phase에서 transferred될 data가 encrypt될 수 있도록 한다.
- initial handshake
- authentication and shared secret establishment
- transport of encrypted data
- authentication and encrypted data exchange
IPsec
IPsec ( = internet protocol security)
= framework of open standards for ensuring authentication, encryption and data integrity on the network layer
=(network layer에서 operate하기때문에) can protect both the data within the packet & L3 information (e.g., IP address) in each packet.
IPsec의 주요 강점은 - securing the network connection without the necessity of modifying any application on the clients or servers.
단점은 - provides less control and flexibility for protecting specific applications
IPsec protocol은 made of two main phases:
(1) first phase - represented by IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2) “아이크” protocol. uses UDP prtocol on the port 500 through which all messages run (covering initial handshake, authentication and shared secret establishment)
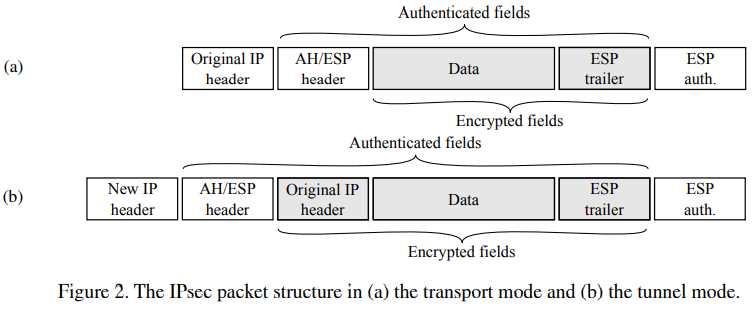
(2) second phase - two protocols are used - AH(Authentication Header) and ESP(Encapsulating Security Payload). 원래 ESP에 data confidentiality를 제공하는 부분에 authentication이 없어서 AH가 함께 사용되었었지만, 현재는 ESP에 authentication이 포함되어있어, AH의 중요도가 덜 중요해졌다. 그러나 아직 ESP가 manage하지 못하는 authentication부분은 AH가 처리한다.
ESP protocol은 IPsec의 main protocol이다. data confidentiality, origin authentication, connectionless integrity, anti-replay service, limited traffic flow confidentiality를 제공한다.
ESP가 each transferred packet에 header와 trailer를 추가한다. ESP와 AH는 두 가지 mode로 operate할 수 있다 - transport and tunnel.
tunnel mode : 새로운 IP header 생성 - the new IP header is for each packet with endpoints of the tunnel as the source and destination addresses.
transport mode : 기존의 IP header가 사용된다.
IPsec site to site VPN tunnels explained (by CBT Nuggests) : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CuxyZiSCSfc
what is IPsec? (by CBT Nuggests) : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-JrXllTuI2s
TLS
= Transport Layer Security.
= is based on the Secure Sockets Layer version3 (SSLv3) protocol.
=provides transport level security directly on top of the TCP protocol. 그리고 digital certificates를 통해서 specifically provides: confidentiality, data integrity, non-repudiation, replay protection and authentication
최근에 network communication의 보안을 확보하기위해 가장 보편적으로 사용되는 protocol이다. TLS는 HTTP, FTP, SMTP session들을 secure하고 VPN(virtual private network) or Voice over IP(VoIP)을 위해 사용된다.
TLS protocol의 design은 layered되어 있고 여러개의 sub-protocol들로 구성되어있으며, configurable and replaceable cryptographic algorithm으로 구성되어 있음.
Record protocol
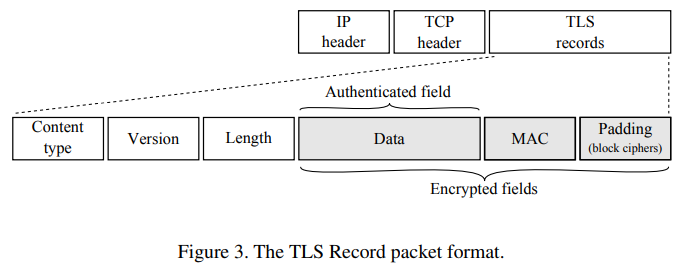
Record protocol은 TLS의 가장 중요한 부분이다. Record protocol acts like an envelop for application data as well as TLS messages.
application data의 경우, Record Protocol은 data를 optionally compressed fragments로 나누는 역할을 맡는다. record로 fragments를 더하는것은 MAC(Message Authentication Code)으로 인해 complement된다.
다음 그림을 보면, 어떤 security algorithm이 select되냐에 따라서 fragment와 MAC이 함께 encrypt되어서 하나의 TLS record로 전송된다.
(1) first phase : during the first phase of a TLS connection, communication parties are usually authenticated (server authentication이 더 자주 보임) using an X.509 certificates chain. (alternatively, previous connection은 authentication없이 resume될 수 있다.) TLS message exchanged during this phase are encrypted and do not contain MAC until the shared keys are established and confirmed.
(2) second phase : these keys are used directly by the Record Protocol, which is based on the selected algorithms ensuring communication security.
Secure Shell protocol (SSH)
= exists as a separate application on top of TCP. TLS protocol과 비슷하게 secure shell protocol (SSH)는 TCP위에 하나의 application으로 따로 존재한다.
= uses a client-server model where the server usually listens to the TCP port 22.
=원래 unsecured Telnet connection을 대신해서 remote login access를 제공하기위해 만들어졌었다. 지금은 remote login과 shell 외에도, SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP)와 Secure Copy (SCP) protocol를 사용하거나 VPN을 통한 file transfer를 제공한다.
=provides user and server authentication, data confidentiality and integrity and optionally compression.
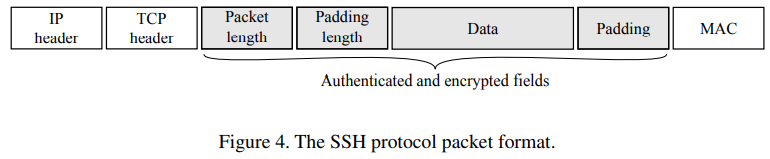
=3개의 protocols로 구성되어있음. 이중에 가장 중요한것은 Transport Layer Protocol. 이 protocol provides the establishment of the whole connection and its management. it defines the SSH packet structure (다음 그림 참고)
The MAC code is computed on a plaintext payload together with the packet length, the padding and a continuously incremented sequence number not present in the packet itself. Other SSH protocols are the User Authentication Protocol and the Connection Protocol for multiplexing multiple logical communications channels
(1) first phase: TCP connection is established and information about preferred algorithm is exchanged. authentication동안, a server sends its public key which must be verified by the client (using a certification authority or manually through a different channel) The shared keys are subsequently established and confirmed. all following packets are then encrypted and authenticated
BitTorrent
= application protocol for peer-to-peer network communication for sharing large amounts of data over the Internet
= security issue가 떠오르면서 ISP에서 BitTorrent type of traffic을 제한하기 시작했다. MSE(Message Stream Encryption) algorithm (aka PE (Protocol Encryption))이 obfuscation algorithm역할을 수행해서 BitTorrent traffic을 인식하기 어렵게 만든다. obfuscation외에도 communicating peers에게 some level of confidentiality와 authentization을 보장해준다.
MSE = transparent wrapper for bidirectional data streams over TCP which prevents passive eavesdropping and thus protocol content identification. MSE는 active man-in-the-middle attacks과 port scanning에 대비하는 limited protection을 제공하도록 설계되어있다 by requiring a weak shared secret to complete the handshake.
The major design goal was payload and protocol obfuscation, not peer authentication and data integrity. Thus, it does not offer protection against adversaries which already know the necessary data to establish connections (that is the IP/port/shared secret/payload protocol).
(1) first phase: follows a TCP three-way handshake and starts with a newly generated Diffie-Hellman (DH) public key exchange (together with random data padding for better obfuscation). The shared key is computed by the DH key and combined with hashed information about the requested data which acts as a pre-shared secret. The packet’s payload is completely encrypted by a RC4 stream cipher after successfully confirming the shared key.
Skype
= peer-to-peer based VoIP application providing not only video chat and voice calls, but also an instant messaging and file exchange service.
= Skype에서 어떤 protocol이 사용되는지는 public하게 알려지지는 않아있다.
the main reason for this is network data obfuscation to make the detection of Skype traffic more difficult, which is similar to the BitTorrent protocol
= skype protocol operates over both UDP and TCP protocols depending on network characteristics. (만약 firewall 때문이든 UDP가 사용될 수 없는 상황이라면, TCP위로 data traffic이 수행된다.) Skype sends both signallying and data traffic over TCP. When TCP is used, the connection is usually established over port 80 or 443, which masks Skype traffic as standard web traffic.
skype는 TLS protocol (over TCP port 443) and proprietary protocol (over port 80)를 사용해서 각 communicating peer와 함께 생성한 traffic의 securing & obfuscating을 수행한다. TLS is also used in communication with other Voice over IP solutions, where it is used for protecting Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) messages. Skype uses a proprietary protocol for communication over UDP. To offer a reliable connection, UDP packets contain an unencrypted header with a frame ID number and function mode fields. The encryption in UDP connections is used only for obfuscation and not for confidentiality; therefore, there is no generated shared secret, only a proprietary key expansion algorithm.
UDP connection은 two phases로 나뉘는 general scheme을 따르지 않는다. (initialization phase없이 encrypted data가 바로 transfer된다.)
Extracting information from encrypted traffic
Unencrypted initialization phase
initialization phase에서 exchange되는 data는 encrypt되어있지 않다. 그래서 이들이 쉽게 extract되어서 network traffic monitoring에 사용될 수 있다.
Generally two types of information common to most protocols can be extracted:
the connection itself - its properties exchanged in the initial handshake
initial handshake동안 connection의 parameters가 negotiate된다. (e.g., cipher suites and which protocol version is used, etc…) connection properties가 dynamic setting으로 설정되기때문에 backward compatibility for different versions of software가 가능하고 established security policies를 기반으로 different level of security를 설정하는데에 사용될 수 있다. some examples are data authentication과 compression in addition to encryption itself.
The list of possible identifications, with references to algorithm specification for IPsec, TLS, SSH and other protocols, can be found in IANA Protocol Registries [40]. All of this information can be used for proper connection characterization and correct parsing of other packets in the rest of the connection
initial handshake로 부터 얻는 information의 사용 case : client fingerprinting based on the provided cipher-suites.
-> A large amount of cipher-suites types exists, which usually are not all implemented by the client’s applications. Therefore, each application specifies the supported cipher-suites and also prefers using them during the initial handshake. 이를 통해 specific operating system, web browser 그리고 다른 application들을 passive하게 distinguish할 수 있다. An example of such client fingerprinting, based on the SSL/TLS initial handshake, is presented by applications from SSL Labs [61] and p0f module [54].
-> extracting the Server Name Indication (SNI) [17] can be used by a home router’s firewall to filter traffic. The unencrypted initialization phase is often used to recognize encrypted traffic and, the authentication information might be utilized to detect and prevent man-in-the-middle attacks on a network-wide level.
communicating peers’ idenfitiers which are exchanged in the authentication phase
authentication phase에서 exchange되는 것들을 활용하는 cases:
unique identifiers of one or both communicating peers (관련 additional data가 supplement되어있을수도)
e.g. SSH protocol의 authentication protocol에서는, server sends its public key to the user, then the user must validate the key and verify that the server knows the appropriate private key. 각 SSH server에 unique(almost)한 information이기때문에, server changes나 또는 man-in-the-middle attacks를 감지할 수 있다. (passive network traffic monitoring)
monitoring the authentication phase of the SSL/TLS protocols
The server, and optionally even the client, sends their X.509 certificates [24] to each other to verify their identities in this phase. This certificate contains a public key signed by the certification authority which is supplemented with information about the peer and issuer.
passive certificates를 monitoring함으로서 communicating peers를 identify하는것 외에도 이 certificates가 valid한지, 그리고 local security policies를 fulfil하기 위해 proper security algorithm을 포함하고있는지를 확인할 수 있다.
SSL/TLS certificate properties에 관한 연구: Holz et al. [38]
invalid한 certificate들이 존재한다.
certification authorities에 관한 연구: Durumeric et al. [30]
Encrypted data transport phase
network traffic에 관한 정보는 communicating parties사이에서 transport되는 encrypted data로부터 extract될 수 있다. transport phase동안 exchange되는 packets에서부터 얻을 수 있는 정보는 매우 제한적이다. packet 자체에 대한 정보 - length 또는 authentication field - 이기때문에 network traffic monitoring에 바로 도움이 되진못하지만, 다음 두 가지 methods를 통해 more suitable data를 얻을 수 있다.
(1) first method - direct traffic decryption을 사용하는 방법이다. 만약 shared secret of the connection을 알고있으면 수행 할 수 있다. decryption can be used in networks on the servers’ side where organizations know the private key of the connected server. 그러나, 이런 decryption would be impossible if algorithms we used ensure forward secrecy. (what is forward secrecy???)
(2) second method - traffic features extraction을 기반으로 하는 method이다.
Miller et al [56] - monitored the size of TLS encrypted packet sequences. 이 data를 바탕으로, 여러가지 predictive model을 사용해서 they are able to identify a specific web page and deduce its content even though the traffic is encrypted.
Koch와 Rodosek [49] - 이 방식을 통한 SSH traffic analysis
Hellemons et al. [37] - focused on intrusion detection in SSH traffic