Parallelism
Parallelism with Multiprocessing
Parallelism
- 완전한 동일한 타이밍(시점)에 task 실행.
- 다양한 파트로 나눠서 실행.(나눠서 구하고 취합)
- 멀티프로세싱에서 CPU가 1 Core인 경우 만족하지 않음.
- deep learning, bitcoin 채굴 등에 사용될 수 있음.
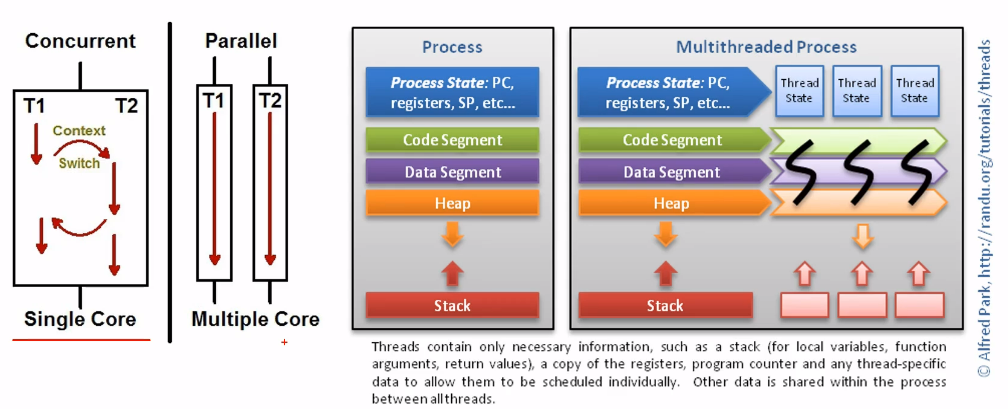
Process vs. Thread 차이 비교
- 독립된 메모리(process), 공유된 메모리(thread)
- 많은 메모리 필요(process), 적은 메모리(thread)
- 좀비(dead) process는 생성 가능성이 높지만, 좀비(dead) thread 생성은 쉽지 않음.
- 오버헤드 큼(process), 오버헤드 작음(thread)
- 생성/ 소멸 다소 느림(process), 생성/소명이 상대적으로 빠름(thread)
- 코드 작성이 쉬움/ 디버깅 어려움(process), 코드 작성이 어려움/디버깅 어려움(thread)
- Process에서는 code, data, heap, stack 모두 개별적으로 만들어짐.
- Thread의 경우에는 stack만 개별적으로 만들어지고 나머지(code, data, heap)은 process내 thread들이 share함. Local variables, function arguments, return values와 같은 stack의 요소들, copy of the register, programing counter, 그리고 그 외 thread-specific data를 thread에 개별적으로 생성하여 개별적인 scheduling에 따라 task를 수행할 수 있도록 한다.
주로 사용되는 함수는 terminate(), join(), is_alive(), 등이 있다. 특히 join은 개별적으로 실행되는 sub-process들이 모두 같은 시점에 끝나도록 ‘join’해주는 역할을 수행한다.
from multiprocessing import Process
import time
import logging
def prof_func(name):
print('Sub-Process {}: starting'.format(name))
time.sleep(3)
print('Sub-Process {}: finishing'.format(name))
def main():
# Logging format 설정
format = "%(asctime)s: %(message)s"
logging.basicConfig(format=format, level=logging.INFO, datefmt="%H:%M:%S")
# 함수 인자 확인
p = Process(target=prof_func, args=('First',))
logging.info('Main-Process: before creating process')
# 프로세스
p.start()
logging.info('Main-Process: during process')
logging.info('Main-Process: joined process')
p.join()
# 프로세스 상태 확인
print(f'process p is alive: {p.is_alive()}')
# main 시작
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Process 수행 시, process id와 process name을 확인하기 위해 다음과 같이 os의 getpid() 함수와 multiprocessing의 current_process()를 사용할 수 있다.
from multiprocessing import Process, current_process
import os
import random
import time
# 실행
def square(n):
time.sleep(random.randint(1,3))
process_id = os.getpid()
process_name = current_process().name
result = n * n
print(f'Process ID: {process_id}, Process Name: {process_name}')
print(f'Result of {n} squared: {result}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 부모 process 아이디
parent_process_id = os.getpid()
print(f'Parent process ID: {parent_process_id}')
# process 리스트 선언
processes = list()
# process 생성 및 실행
for i in range(1,50): # 10~100 실행
# 생성
t = Process(name=str(i), target=square, args=(i,))
# 배열에 담기 (하나의 리스트로 모두 담아서 한번에 join해주려고)
processes.append(t)
# 시작
t.start()
for process in processes:
process.join()
# 종료
print('Main-Process Done.')
공유 자원의 활용
프로세스 메모리 공유의 예시
from multiprocessing import Process, current_process, Value, Array
import os
# 실행함수
def generate_update_number(v: int):
for _ in range(50):
v.value += 1
print(current_process().name, "data:", v.value)
def main():
# parent process id 확인 (디버깅을 위해 꼭 필요)
parent_process_id = os.getpid()
# 출력
print(f'Parent process ID: {parent_process_id}')
# 프로세스 리스트 선언
processes = list()
# 프로세스 메모리 공유 변수
# 공유 변수의 type(i for int, c for char, 등등), 값, 등등 엄격하게 선언되어야 함.
share_value = Value('i',0)
# 공유 변수가 리스트일때는 다음과 같이 Array를 활용한다.
share_numbers = Array('i', range(50))
# 위 Value, Array외에 아래 두 library들도 사용 가능 함.
# from multiprocess import shared_memory 사용 가능 (python 3.8이상 부터)
# from multiprocess import Manager 사용 가능
for _ in range(1,10):
# 생성
p = Process(target=generate_update_number, args=(share_value,))
# 배열에 담기
processes.append(p)
# 실행
p.start()
# join
for p in processes:
p.join()
# 최종 프로세스 부모 변수 확인
print('Final Data in parent process', share_value)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
프로세스 통신 구현
queue 또는 pipe를 통해서 worker(sub process)에서 실행한 값을 부모(main process)에게 전달
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue, current_process
import time
import os
# 실행함수
def worker(id, baseNum, q):
process_id = os.getpid()
process_name = current_process().name
# 누적
sub_total = 0
# 계산
for i in range(baseNum):
sub_total += 1
# Produce
q.put(sub_total)
# 정보출력
print(f'Process ID: {process_id}, Process name: {process_name}, ID: {id}')
print(f'Result: {sub_total}')
def main():
# 부모 process id
parent_process_id = os.getpid()
# 출력
print(f'Parent process id: {parent_process_id}')
# 프로세스 리스트
processes = list()
# 시작시간
start_time = time.time()
# Queue 선언
q = Queue()
for i in range(5): # 1~100사이 값으로 설정
# 생성
t = Process(name=str(i), target=worker, args=(i, 100000000, q))
# 배열에 담기
processes.append(t)
#시작
t.start()
# join
for process in processes:
process.join()
# 순수계산 시간
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))
# 종료 flag
q.put('exit')
total = 0
# 대기
while True:
tmp = q.get()
if tmp == 'exit':
break
else:
total += tmp
print('Main-Processing Total Count={}'.format(total))
print('Main-Processing Done.')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Multiprocessing에서 shared memory는 Python multiprocessing documentation 참고
References
- 프로그래밍-파이썬-완성-인프런-오리지널