How VoIP works
Essential terms
codec: HW or SW-based process that compresses and decompresses large amounts of data. often used in applications to play and create media files for users or send media files over a network. codec’s main job is data transformation and encapsulation for transmission across a network.
lossy codec vs. lossless codec: lossy codecs reduce file’s quality in order to maximize compression and minimizes bandwidth requirements for media transmission. lossless codec uses data compression algorithm that enables compression and decompression of files without loss of quality and is good for preserving the original quality of the file but at the expense of higher bandwidth requirements (lossless codecs are good fit for film, video and photo editing)
voice codecs: encodes voice(analog signal) into a digital data stream using fewer bits than the original representation, and then reconstructs the voice signal through decoding. This enables vast amounts of simultaneous voice calls over cellular networks and ensures low latency in voice communication to provide natural conversation flow.
EFR(Enhanced Full Rate, 1996) –> AMR-WB(Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband, 2001) extended audio bandwidth from 300~3.4 kHz to 50~7 kHz and improved intelligibility and naturalness of voice –> EVS(Enhanced Voice Services, 2014) pushed audio bandwidth up to 20 kHz with higher quality for any audio including music
Today(as of June 2022), EVS codec is widely deployed in devices and networks around the world.
For the future (according to Nokia), to enable lifelike acoustic experiences, Immersive Voice and Audio Services (IVAS) codec is developed to address spatial voice and sharing of immersive experiences.
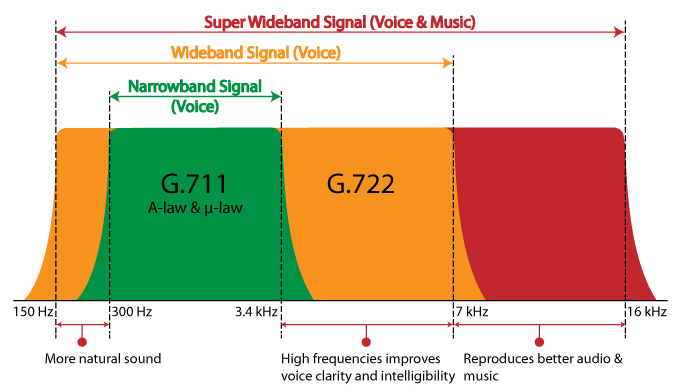
range of frequency to consider: phone call vs. face-to-face sound different because phone doesnt pick up all the frequencies that human voice or music or any other sound hits. human speech is between 80 ~ 14 kHz. (lower the frequency, deeper the sound) phone audio typically involves two bands: narrow bands and wideband
narrowband: covers audio frequencies ranging between 300 ~ 3.4 kHz
wideband: covers audio frequencies ranging between 50 ~ 7 kHz. when you talk in wideband audio (also known as HD voice), you’ll be able to hear an expanded range of pitches most closely resembling an in-person conversation. wideband improves the sampled and transmitted audio spectrum, making the audio sound better.
sample rate: known as sample frequency, it refers to the audio samples taken per second. every individual sample will tell you the signal waveform’s total amplitude value over a specific period. higher the sample rate, better the audio quality
bitrate: the amount of data that is transferred into audio. audio bitrates mean it captures more sound information per second. generally, a higher bitrate indicates better sound quality. 아무리 quality가 좋은 sound이여도 sample rate이나 bitrate가 낮으면 it will sound bad.
bandwidth: the speed the you receive or send data. Bandwidth is the bottleneck. VoIP codecs aim to conserve bandwidth while maintaining good sound quality.
transmission rate: number of samples that are transmitted every second
VoIP codecs: voice codec that convert audio signals into digitized packets an transmits them through LAN(Local Area Network) To prioritize these data packets, might need to enable Quality of Service(QoS) to allow VoIP data to take priority over less critical traffic. The difference between different VoIP codecs is the way audio is compressed. How the file is compressed determines how much bandwidth is required for transmission.
3 types of VoIP codecs:
G.711
ITU introduced G.711 codec in 1972. This codec can squeeze 16-bit samples into 8 bits through logarithmic compression. As a result, the compression ratio becomes 1:2. The bitrate for both directions is 128 kbit/s (64 kbit/s for a single path), which is a lot. While you get superior sound quality, the bandwidth requirement is relatively high. Plus, this codec doesn’t support multiple phone calls as adequately as other codecs like the G.729.
G.722HD
G.722 is a high-definition codec, which means it’s wideband. ITU approved this codec in 1988, and since the patent has expired now, it’s free to use for everyone. This codec helps improve speech quality without perceivable latency. HD voice has double the sample rate of G.711 at 16 bits. The transmission rate remains the same at 64 kbit/s.
G.729
G.729 is codec with low bandwidth requirements and acceptable audio quality. This codec encodes the audio in frames. Each frame is ten milliseconds long and contains 80 audio samples. The bitrate for one direction of this non-HD codec is 8kbit/s. Since the compression is higher, you’re able to make more calls from your network at once. That said, a few VoIP providers may not support the G.729 codec. Music and other non-verbal audio can sound choppy.
jitter : variations in packet arrival time. occurs because of network congestion, timing drift, or route changes (computed as the standard deviation of delay)
Jitter caused by different packets of the same conversation have different queue lengths or different routes when they are transmitted over the network. In order to avoid the reduction of voice quality, jitter has to be removed before replaying at the receiver. In order to reduce jitter, a de-jitter is used at the end user to delay the initiation of the replay process.
jitter buffer : In VoIP, jitter buffer is a shared data area where voice packets can be collected, stored and sent to the voice processor in evenly spaced intervals. Jitter buffer is located at the receiving end of the voice connection, intentionally delays the arriving packets to that the end user experiences a clear connection with very little sound distortion. there are two kinds of jitter buffer - static vs. dynamic.
Static is hardware-based and is configured by the manufacturer.
Dynamic is software-based and can be configured by the network administrator to adapt to changes in the network’s delay.
packet loss : effect of packet loss on speech quality depends on factors like - loss rate, codec type, packet size, packet loss concealment (PLC) algorithm. Loss pattern may be random or bursty.
playout delay: 한 frame의 playout delay는 “sender쪽에서 frame이 capture된 시간에서 부터 receiver쪽에서 frame이 render되기까지 delay 되는 시간 “로 해석된다.
“Total amount of time experienced by an audio packet from the time instant it is generated at the source and the time instant it is played out at the destination”
consists of:
- time needed to collect an audio sample and to prepare it for transmission
- network delay
- buffering time (=time that a packet spends waiting in the destination buffer before it is played out.)
playout delay = expected render time(frame) - expected capture time(frame)
playout delay값에 Min과 Max가 존재함.
Min and Max playout delay represents the minimum and maximum delay that can be seen on a frame. this restriction range
https://webrtc.googlesource.com/src/+/main/docs/native-code/rtp-hdrext/playout-delay/README.md
carrier aggregation: RAN(Radio Access Networks)와 user devices에 존재하는 software functionality인데, 이 software 기능을 통해서 MNO(mobile network operator)가 다양한 frequency allocation의 radio cell들의 capabilities를 통합해서 end user experience를 향상시킬 수 있다.
LTE-advanced network에서 이미 활용되어서 Gigabit-LTE(user data rates of more than 1Gbps)를 가능하게 한다. 5G networks에서는 multi-Gigabit-5G를 가능하게 하여 약 4Gbps 이상의 user data rates를 가능하게 할 수 있다.
5G Carrier Aggregation is also capable of improving the geographic availability, more commonly referred to as coverage of high data rates.
https://www.nokia.com/about-us/newsroom/articles/5g-carrier-aggregation-explained/
carrier: each frequency layer which has specific characteristics in terms of coverage (the range around the antenna where signals can still be received) and capacity (bandwidth, data rates, throughput). Carrier aggregation plays a vital role in turning the cumulative spectrum bandwidth of variety of frequency allocations into higher data rates for the end users.
carriers in the higher frequency ranges typically provide greater capacity, while carriers in the lower range provide wider and deeper coverage.
coverage is affected by the two following factors:
- lower frequencies translates into larger wavelengths, which propagates better and reach deeper indoors
- lower frequency bands are typically used in FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) mode, which has higher uplink signal strength compared to TDD (Time Division Duplex) mode, which is almost exclusively used for cellular allocations above 2.5 GHz.
Packet Loss Rate (PLR): percentage of packets which have not reached their destination. these packets could have been dropped over the network. 이런 packet들이 voice quality degradation 영향을 끼칠 수 있음.
왜 PLR이 발생하는지? there are many reasons such as link failure, congestion, buffer overflow or wrong route, 등등
Packet Loss Concealment (PLC): deliver되지 못한 packet들을 receiver쪽에서 restore하는 역할을 수행한다. For the VoIP, PLR characteristics are bursty.
Delay: average time that a voice packet is transmitted from the source to destination. VoLTE의 경우, 3GPP에서 100 milisecond(ms)를 넘지 않도록 제안한다. ITU-T에서는 일반적인 network에서 400 ms를 넘지않도록 제안한다.
In order to compute one-way delay of voice packet, ITU-T Recommendation provides the E-model for narrow audio band and Wideband E-model for wide audio band. For the real-time services such as VoIP or Video calls, the end to end delay shouldn’t exceed 150 ms for a better quality.
SRTP(Secure Real Time Transport Protocol) : SRTP is based on the RTP and it denotes a technical process for the encrypted transfer of multimedia data(e.g., speech) via existing networks.
SRTP는 internet telephony (e.g., VoIP or Voice over Internet Protocol)를 위해 활용되어서 multiple conversation participants사이에서 telephone data가 송/수신 되는 동안 eavesdrop-secure transfer 방식을 제공할 수 있다.
(e.g., NFON이라는 회사의 voice encryption system은 Transport Layer Security Standard (TLS)와 SRTP Standard를 사용한다.)
is a method of communication for making calls over a broadband Internet connection as an alternative to regular calls made…
PSTN(Public Switched Telephone Network): PSTN is known as the traditional phone network. The arrival of Voice over IP (VoIP) technology – essentially, transmitting voice calls over the Internet rather than the PSTN – challenged traditional telephony and fundamentally changed how people communicate.
Voice signals can travel over this circuit. When the caller speaks into his handset, the caller’s phone translates the sound waves into electrical signals. These are transmitted over the PSTN (converted to optical signals for part of the way, so they can travel via fibre optic cables), and the phone at the other end of the line then translates the received signals back into sound.
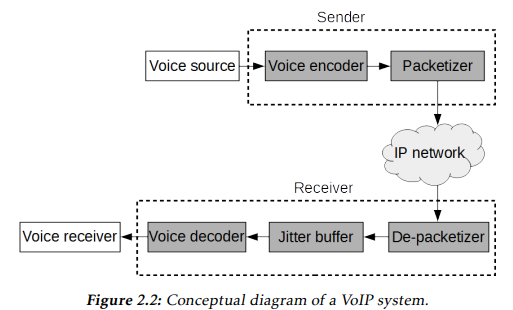
VoIP system structure & roles
three major components:
1. sender
encoder(codec)
voice-codec이 voice stream을 speech frame 형태로 digitalize & compress한다.
여기에서 사용되는 codec마다 다음 사항들이 달라진다:
- sound quality
- required bandwidth
- computational complexity
low rate codec중 하나인 G.729D codec 관련 내용:
“The codec operates on 10 ms frames and extracts prediction parameters so that the decoder can recreate the current frame based on the previous one. The implication of this is that losing one speech frame affects consecutive frames as well. To compensate the codec uses packet loss concealment which tries to maintain the characteristics of the signal while gradually decreasing its energy when a frame is lost. How to detect missing frames is not given by the standard but dependent on the implementation.”
packetizer
network의 congestion을 방지하기 위해, several speech frame들을 모아서 packet의 payload로 packetize한다. (e.g., RTP packets) Encoded speech frames를 packetize해서 network을 통해 minimal delay로 high throughput을 구현하도록 하는 역할을 한다. 그리고 이때 packet에 network에서 요구하는 header들이 추가 된다.
- 12 bytes RTP header
- If a VPN solution is used, as discussed in Section 2.1, the DTLS header adds roughly 20 bytes depending on the configuration
- 8 bytes UDP header
- 20 bytes IP header
- Link layer header, for Ethernet a MAC header of 18 bytes is added
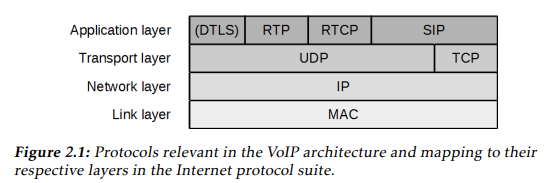
[참고]Layer별 VoIP관련 protocols:
2. network
network에서 다양한 종류의 impairments가 introduce된다. (such as packet loss, delay and jitter)
network에서 이런 영향을 받은 상태로 packet들이 receiver에게 전송된다.
3. receiver
de-packetizer
receiver쪽에 도착한 packet은 de-packetizer로 인해 header들이 제거되고 speech frame들이 extract된다.
network내 transmission을 통해 전송되는 packet들은 처음 sender쪽에서 보낸 timing과는 다르게 receiver쪽에 도착할 수 있다. (UDP가 사용된 경우에는 순서가 바뀌어 도착할 수 있음.)
그래서 다음 단계인 jitter buffer를 통해 incoming packet들을 buffer하고 continuous and ordered stream으로 보내질 수 있도록 조정한다.
jitter buffer
frame 상태로 jitter buffer에 보내져서 network내 impairment로 인해 발생된 jitter를 counteract한다. 여기에서 추가적인 delay가 발생한다.
buffer가 작은 경우 delay가 작지만, transport delay variation을 충분하게 absorb하지 못해서 packet loss가 발생할 수 있다. 그래서 buffer의 size가 상황에 맞게 변동될 수 있는 adaptive buffer를 사용하면, current scenario를 estimate하고 주어진 optimization rule에 따라 적절한 buffer size로 설정되어 buffer의 역할을 더 잘 소화할 수 있다. (static buffer보다는 adaptive buffer 선호)
또한 그래서 jitter buffer는 보통 application specific하다. 일반적으로 평가하기 어려운 부분이 있음.
decoder(codec)
마지막으로 speech frame들이 decode되고 output된다. 여기에서 pack loss concealment (PLC)를 사용해서 lost packet에 대해 보상하는 과정을 수행한다.
References
- Parametric Prediction Model for Perceived Voice Quality in Secure VoIP (Andersson, 2019)