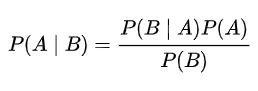Gaussian Processes
Uncertainty
Machine learning method들은 주어진 “training data”를 가지고 그 속에 담긴 pattern을 학습해서 미리 보지못한 미지의 영역의 데이터를 예측한다. Gaussian process는 그 methods 중 하나이고, 다른 method들과는 “uncertainty와의 관계” 관점에서 unique한 점이 있다.
미지의 영역 (즉, machine learning 문제의 해결을 통해 예측하려는 uncertainty 영역)은 발생할 수 있는 outcomes와 이들의 발생 확률 분포로 표현될 수 있다.
Uncertainty를 표현하는 probability distribution은 두 가지로 나뉠 수 있다:
- discrete : finite number of possible outcomes (e.g., rolling a fair sided dice)
- continuous : outcome could be any real number (e.g., unknown height of my favorite character in a cartoon)
Bayesian Inference
Bayes’ inference는 Bayes’ rule을 statistical inference를 위해 응용하는 것이다.
Bayes rule = describe probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event.
Bayesian inference의 공식 definition:
“One of the many applications of Bayes’ theorem is Bayesian inference, a particular approach to statistical inference. When applied, the probabilities involved in the theorem may have different probability interpretations. With Bayesian probability interpretation, the theorem expresses how a degree of belief, expressed as a probability, should rationally change to account for the availability of related evidence.”
Mathematically, Bayes’ theorem은 다음과 같이 표현된다:
Bayesian inference는 다음 문구로 설명할 수 있다.
Bayesian inference boils down to just a method for updating our beliefs about the world based on evidence that we observe.
여기에서 “our belief”는 probability distribution으로 표현된다. Bayes’ rule에 따라 주어지는 새로운 데이터를 가지고 기존 probability distribution을 업데이트하고 더 나은 “belief”를 만들어 나아간다.
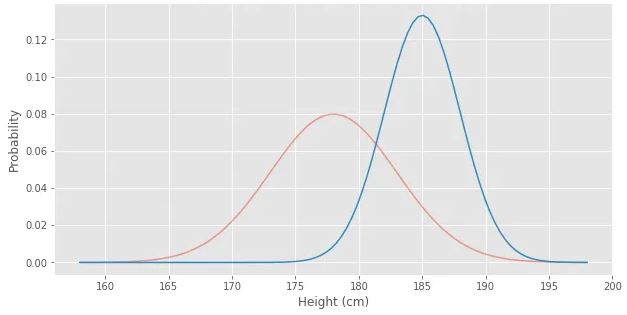
예측하고 싶은 값이 height(cm)과 같이 continuous numeric value에 속한 case를 예시로 본다면, 다음과 같이 probability distribution graph로 표현될 수 있다.
빨간색이 첫번째 “belief”였다면, 새롭게 주어지는 데이터를 가지고 파란색 update된 “belief”를 얻을 수 있다. 예측하려는 값에 대한 probability distribution이다.
이와 비슷한 맥락으로, Gaussian process는 예측하려는 function에 대한 probability distribution이다.
A Gaussian process is a probability distribution over possible functions
Gaussian process를 활용하여 function에 대한 probability distribution을 표현할 수 있다. 그리고 Bayes rule을 사용하여 training data의 학습을 기반으로 function의 distribution을 업데이트해 나아 간다.
추상적인 예시로 설명을 해보자면,
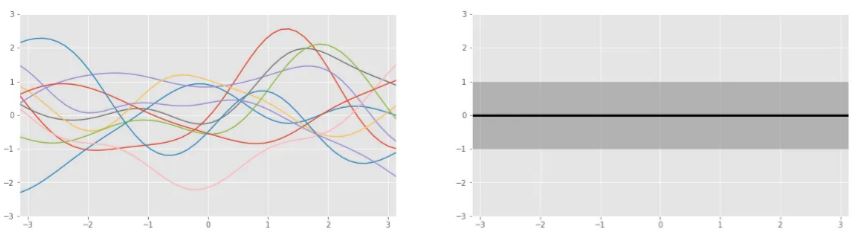
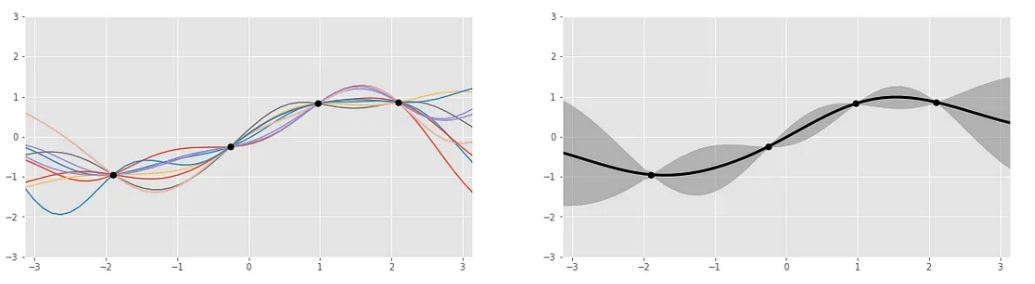
다음 graph들은 unknown function과 이들의 Gaussian process의 mean & standard deviation을 보여준다. training data를 통해 분석 및 업데이트가 진행되기 전의 “prior belief”라고 할 있다. 오른쪽에는 best guess로 middle of real number인 0을 mean(중심)으로 두고, 왼쪽에는 넓은 범위에 퍼져있는 possible function들이 그려져있다.
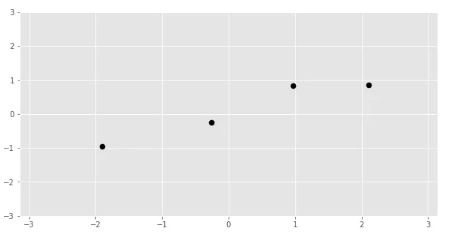
만약 다음과 같이 “evidence” 역할을 할 training data가 주어진다면,
다음과 같이 Baye’s rule을 통해 “prior belief”를 update할 수 있다. 이 “posterior belief”는 주어진 training data를 기반으로 찾은 훨씬 더 narrow된 possible function들이다. possible function의 mean은 주어진 training data와 모두 intercept라고 standard deviation을 양쪽 끝 미지의 영역으로 갈수록 더 넓어진다.
The updated Gaussian process is constrained to the possible functions that fit our training data.
Gaussian Process의 장단점
- 👍 Gaussian process의 장점은 모르는 영역을 인식하고 있다는 것이다.
Gaussian processes know that they don’t know. This is a direct consequence of Gaussian processes roots in probability and Bayesian inference.
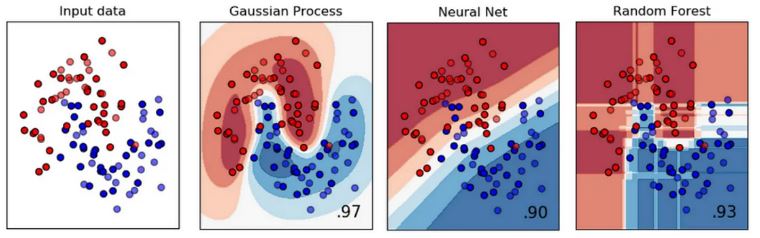
당연하게 느껴질 수도 있지만, 다른 machine learning method들은 이 장점이 없는 경우가 많다. 아래 그림에서 보이듯이, neural net과 random forest와는 다르게, Gaussian process를 training data에서 멀어질수록 contour 색이 옅어진다 (즉, 주어진 training data에서 멀어질수록 uncertainty가 증가한다.)
높은 classification accuracy로 알려진 neural net과 random forest는 training data에서 멀어져도 높은 certainty를 유지한다. 이런 method들은 강력한 성능을 가지고있지만, 종종 미지의 영역에서 “adversarial examples”를 발생시키는 문제를 일으킨다.
Adversarial examples: when powerful classifiers give very wrong predictions for strange reasons.
Gaussian process의 장점이 output에 대한 certainty를 높이기때문에, adversarial case로 부터는 멀리, identity verification이나 security critical use case에는 더 적절한 method가 되도록 한다.
- 👍 Gaussian process는 kernel의 선택에 따라 “prior belief”를 설정할 수 있다.
Gaussian processes let you incorporate expert knowledge via the choice of kernel
Kernel을 어떻게 설정하냐에 따라서 fitted function을 다양한 모양으로 만들 수 있다. Uncertainty 영역에 대한 GP의 generalization은 kernel로 인해 거의 결정 된다고 보면 된다.
- 👎 Gaussian process는 Computationally expensive
Gaussian process는 non-parametric method이다. Parametric approach는 “a set of numbers”에 training data로 부터 얻은 정보를 넣을 수 있다. (e.g. linear regression의 경우에는 단, 두 개의 numbers - the slope and the intercept - 에 approximate function을 만들 수 있는 정보를 넣는다.) Parametric의 경우에는 미지의 영역에 대한 예측을 구하는 inference 단계에서 이 “set of numbers”만 있으면 prediction을 만들 수 있다. (after training, the cost of making predictions is dependent only on the number of parameters.)
Non-parametric의 경우에는 training data 전부를 고려해야 prediction을 만들 수 있다. This means not only that the training data had to be kept at inference time, but also means that the computational cost of predictions scale with the number of training samples.
Deep learning이 dominant한 분야에서도 Gaussian process를 활용할 수 있도록 연구가 진행되고 있다. Deep & convolutional Gaussian process를 통해 high-dimensional and image data를 처리하고, large dataset에도 활용 될 수 있도록 sparse and minibatch Gaussian process로 scalability를 높이는 방안, 등이 있다.
References
- An Intuitive Guide to Gaussian Processes by Oscar Knagg : https://towardsdatascience.com/an-intuitive-guide-to-gaussian-processes-ec2f0b45c71d
- The Gaussian processes framework in Python https://github.com/SheffieldML/GPy
- Baye’s theorem : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayes%27_theorem