HTTPS SNI Classification
논문: Niloofar Bayat, et al. (2021) Deep Learning for Network Traffic Classification
Background
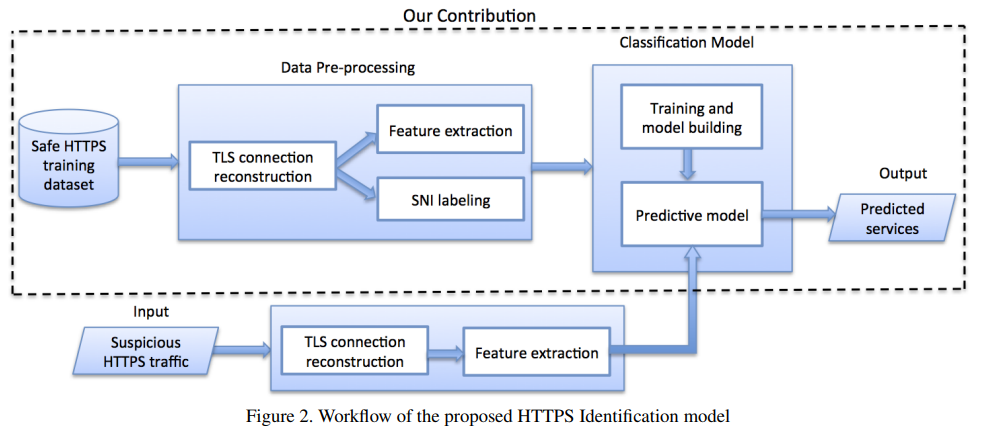
Packet, payload, and inter-arrival time sequences, 등을 기반으로 deep learning architecture의 ensemble을 사용해서 새로운 classification technique를 개발했다. 이 논문의 목표는 HTTPS SNI classification에 deep learning이 접목되면 얼마나 더 효과를 볼 수 있는지 examine해보는 것이다.
encrypted TLS packet data without SNI extension을 data로 사용하고, SNI를 ground truth label로 설정함. SNI가 fake/forged되어있지 않다는 가정하에 deep learning이 얼마나 service identification accuracy를 높일 수 있을지 확인해봄.
기존 research에선 application level의 classification과 traffic type classification이 많이 진행되었음. 이 논문에서 하고자 한것은 traffic의 type을 분류하는 것보다 더 상세한 underlying service name을 분류하는 것임.
e.g. maps.google.com과 drive.google.com을 따로 구분할 수 있어야 함.
통계와 machine learning을 통해 service name 분류를 진행했던 연구 결과가 있음.
저자가 참고한 closely related research works:
- Shbair et al. Efficiently bypassing sni-based https filtering. In Integrated Network Management (IM), 2015 IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on
–> Their proposed statistical framework includes the standard packet and inter-arrival time statistics, as well as additional statistical features related to the encrypted payload. They achieve their best results using Decision Tree and Random Forest classifiers.
- Lopez-Martin et al. Network traffic classifier with convolutional and recurrent neural networks for internet of things. IEEE Access
–> apply RNN and CNN to application level identification problem. Their CNN-LSTM architecture가 사용하는 features: source port, destination port, packet size, TCP window size, inter-arrival times. classification 성능은 Random Forest classifier를 능가한다. 그리고 중요한 한가지 - Large number packets가 필수가 아니라는 것. (5~15 packets만 있어도 충분함)
Data collection & preprocessing
data collection
‘pcap’ files는 packet capture files를 의미한다.
publicly available HTTPS data were collected over 2-week period in 2016
made of 24 raw packet capture (pcap) files, between 4 and 6 gigabytes of data
500K HTTPS flows (from thousands of different services and websites)중에서 이 논문의 research에서는 300K정도의 HTTPS(25GB) flows 사용함.
data preprocessing
-Since a pcap file may contain all different kinds of traffic within a local machine, used SSL filter on Wireshark to obtain HTTPS traffic only
-script를 하나 작성해서 incoming packet과 outgoing packer을 구분짓는 작업을 수행함. (from local machine to specific server & vice versa) 어떻게 했냐면 - 각 TCP connection를 위해 4-tuple를 만듬 (containing source IP, destination IP, source port number, destination port number) source와 destination IP/port가 reserve된 TCP connection들은 하나의 specific server와의 two directions of communication을 의미하기때문에 unify함. 그리고 unknown SNI들은 모두 filter out하고 numbers, dashes, 다른 불필요 character들을 제거해서 remaining label들을 “깨끗하게” 만드는 과정을 거침
-각 connection을 위해 다음과 같은 attributes를 memory에 저장함:
SNI(label)
accumulated bytes
arrival times
packet sizes
payload sizes
feature selection/extraction
이 논문의 feature extraction는 Shbair의 2016년 논문”A Multi-Level Framework to Identify HTTPS Services “를 많이 인용함.
first dataset - stat features
pcap files로부터 첫번째로 generate한 42 statistical features를 Random Forest Classifier의 training & validating에 사용함.
for each group of features - 3가지의 communication directions를 계산함:
• Packet size: {num, 25th, 50th, 75th, max, avg, var}
• Inter-arrival time: {25th, 50th, 75th}
• Payload size: {25th, 50th, 75th, max, avg, var}
second dataset - sequence features
다음 3가지 features로 구성됨 - sequences of packet sizes, payload sizes, inter-arrival times(generated from the TLS handshake that are needed for RNN). 이 feature들은 machine learning network traffic classification에서 기본적으로 사용되는 “standard feature”들임. 각 feature는 meaningful sequence로 구성되어있음.
training data를 위해 local->remote 또는 remote->local의 sequence대신에 combined packet들의 sequences를 사용함. Each length-n sequence corresponds with the first n packets per TCP connection, ordered by arrival time. All shorter sequences are pre-padded with zeros such that each input has the same length.
inter-arrival time의 값에 large variance가 존재하기때문에 standardization, normalization 외에도 log(t)값으로 변환하여 RNN을 훈련시킴. log(t)로 time sequence내의 similarity를 보존하면서 gradient calculation을 throw off하지 않는다.
packet sequence length = n을 어느 수준으로 설정하는지가 매우 중요함. 잘 골라서 balancing해야하기 때문. The longest TCP handshakes in our dataset have tens of thousands of packets. 이렇게 긴 packet sequence length의 경우에는 RNN훈련과정이 너무 오래걸림.
이 논문에서는 relatively short n = 25로 설정함. b/c 너무 긴 sequences yield diminishing accuracy improvements and much slower training time.
현실에서는 sequence 길이가 얼마나 긴지, 그리고 얼마나 자주 매우 긴(TCP handshake가 tens of thousands of packets만큼 긴) case들이 발생하는지에 따라서, 이 논문에서 설정한 n=25를 기반으로 확인된 model performance가 현실에 그대로 반영되기 어려울 수 있지않을까…?
이 논문의 contribution:
DL Model
CNN + GRU(Gates Recurrent Units- a type of RNN the extend the conventional feedforward neural network to sequences of variable length)
apply a one dimensional(1x1) CNN to our time series features to capture dependencies between feature vectors in consecutive time slots.
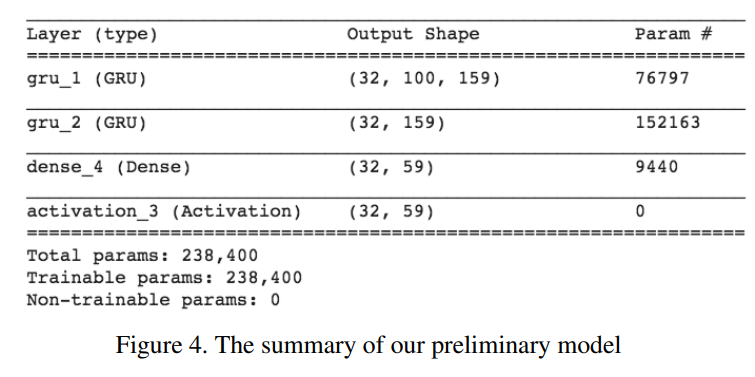
preliminary(baseline) model = model made of the following layers: GRU-1 + GRU_2 + dense_4 + activation_3(softmax)
Evaluation Metrics
accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score for a variety of classifiers를 지표로 평가함. (accuracy는 10-fold cross validation을 통해 사용됨.)
For precision, recall, and F1-score, scikit-learn reports the macro-average which is an unweighted average of the calculated statistic per class.
accuracy = simply the sum of correct predictions over the total number of predictions
Execution environment
hardware - MacOS, 16GB RAM
training and validation run on Google Deep Learning virtual machine(Debian Linux OS instance with 16vCPUs and 60GB RAM)
Results
Preliminary model
RNN trained on packet sequences only
two GRU layers with fc dense layer with softmax activation
baseline architecture was trained for 10 epochs, and we use a batch size of 64, Adam optimizer, and sparse categorical cross entropy loss.
RandomForest만으로 minimum connection(low barrier to entry)의 경우에도 85% 이상의 accuracy 가 확보됨.
Improvements
아래 2 가지 문제 해결을 위해 improvement를 만들었다:
아래 2 가지 문제 해결을 위해 improvement를 만들었음:
첫번째 문제: baseline RNN performs poorly on specific inputs. 특정 input에 관하여 모델의 성능이 떨어짐.
해결: TCP handshake의 payload size와 inter-arrival time feature들을 추가해서 classifier를 훈련시킴.
하나의 모델을 3가지 feature로 훈련시키기 보다는 3개의 모델을 각 feature에 대한 학습을 하게한 뒤, ensemble했음.
각 deep learning architecture가 각자 다른 signal을 알아보도록 학습하면, 세 개의 architecture이 ensemble되면 더 다양한 signal을 알아보는 능력이 더 높아질 것으로 봄.
Our final ensemble classifier simply chooses the class with the highest Softmax probability after averaging across the three individual classifiers.
두번째 문제: baseline RNN has high bias when there are many potential classes. potential class의 개수가 많을 때에 bias가 매우 높음.
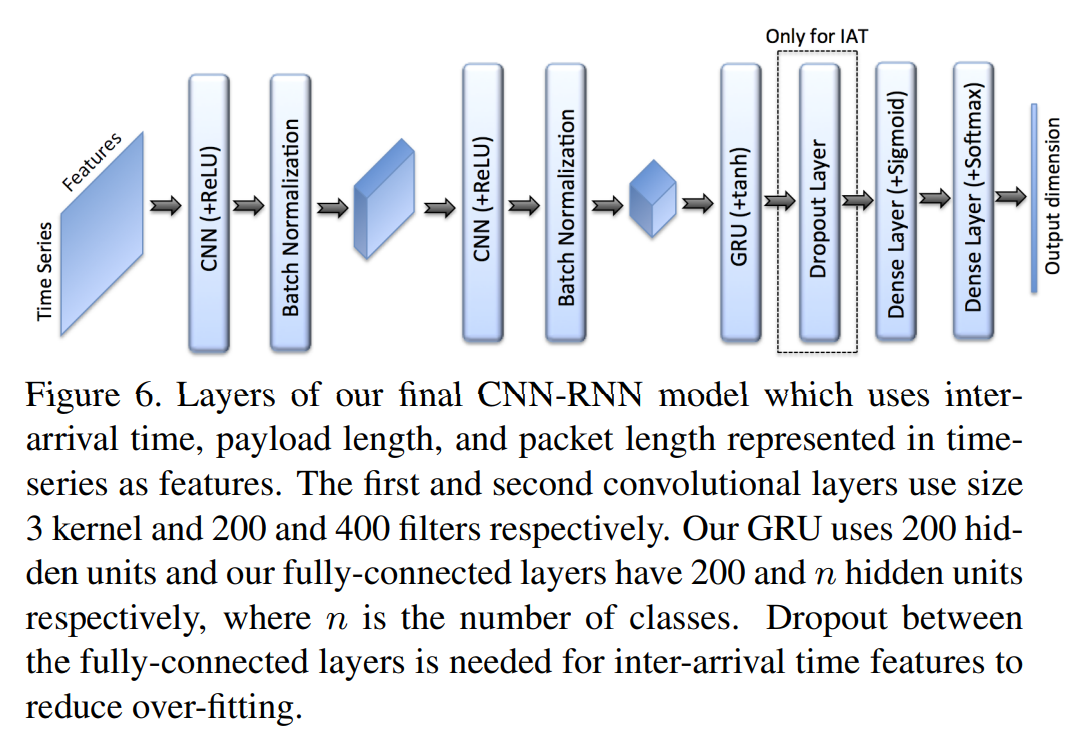
해결: CNN-RNN architecture을 만들어서 모델의 complexity를 높이고, RNN layers에 hidden units를 추가함. 그래서 다음 그림과 같은 구조를 형성함.
We alter our model to include:
- Convolutional layers
- Batch Normalization
- an additional dense layer
더 커진 model의 over-fitting 방지 위해 inter-arrival time data를 학습하는 이 CNN-RNN모델에는 dropout을 추가하고 훈련 속도를 높이기 위해서 GRU layer를 하나 제거함.
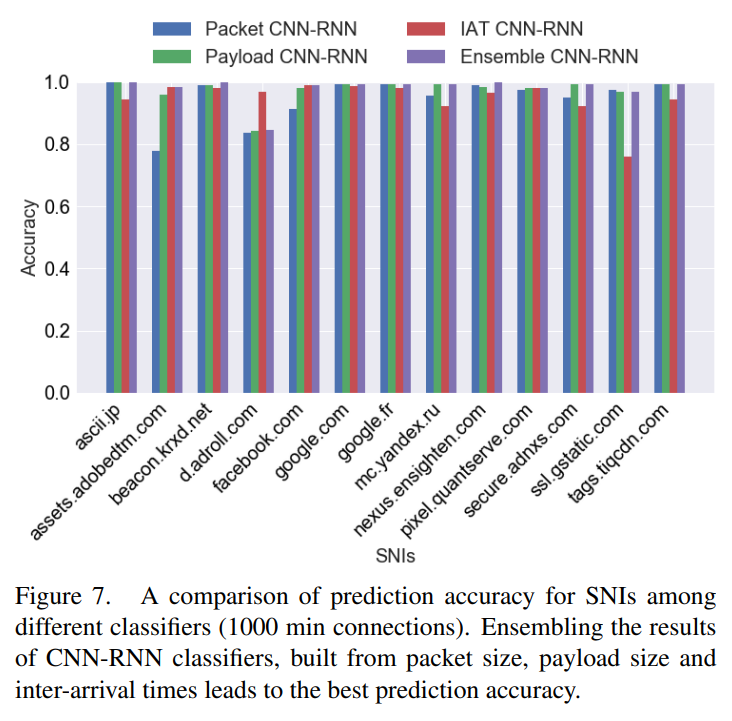
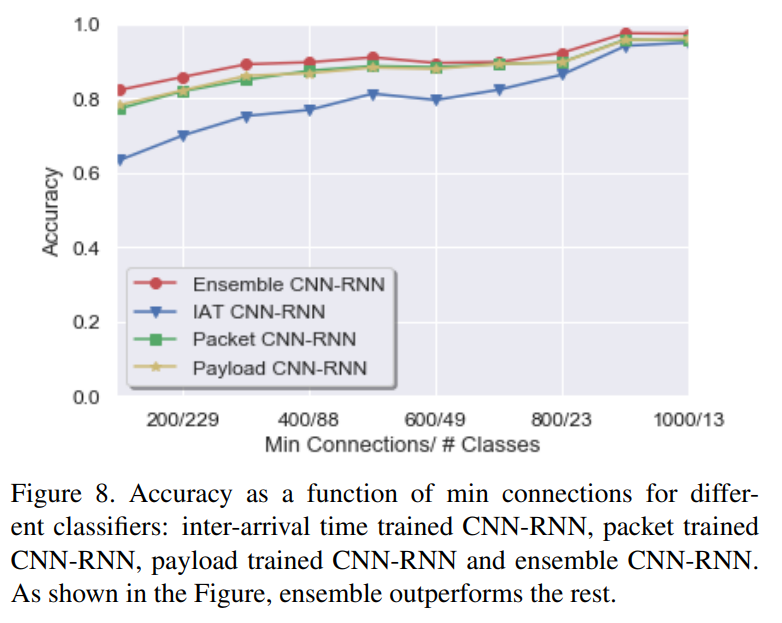
아래 graph에서 ensemble의 효과를 확인할 수 있다.
(보라색 bar : 3개의 models ensembled one)
10 epochs동안 훈련을 진행하기보다, 더 epoch수를 늘리고 대신 Keras의 조기종료를 활용함. (to end training when validation loss does not improve for 5 epochs.) 모델의 성능을 확보하는데에 중요했음 because early stopping is a crucial component to our model’s performance, as lower minimum connections thresholds can require 30+ epochs for validation accuracy to converge.
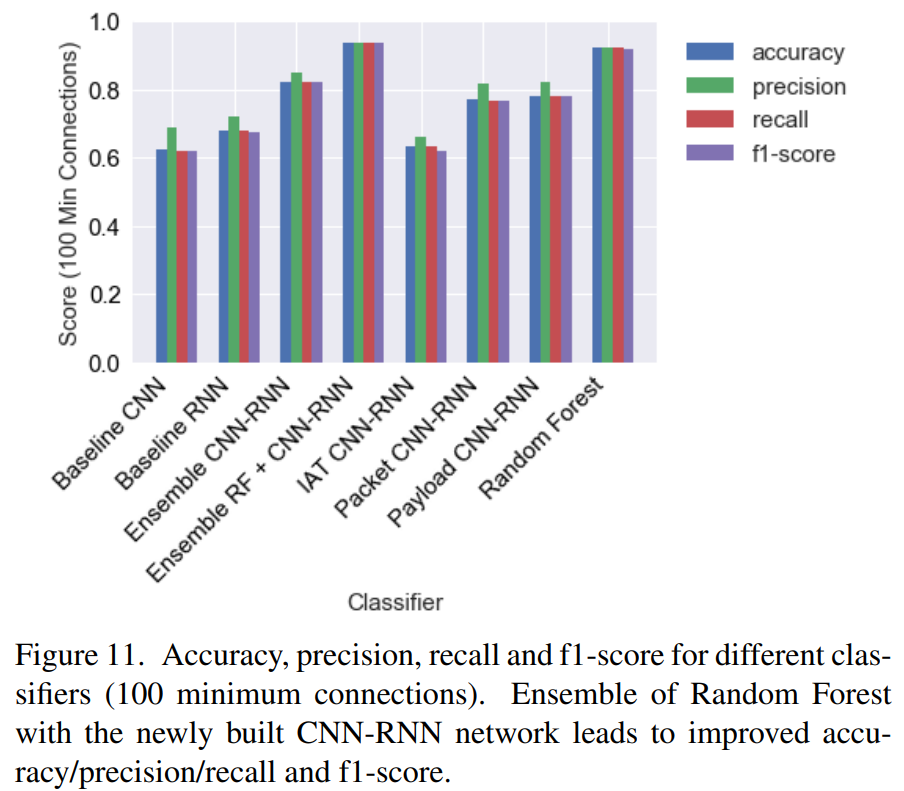
Best Result
이 조건에서 Random Forest Classifier는 92.2%의 10-fold cross validation accuracy를 확보함.
preliminary baseline RNN model은 (trained on packet sequences) 67.8% accuracy를 확보함.
two-layer baseline CNN trained on packet sequences achieves 62.4 % accuracy.
The combined CNN-RNNs for packet, payload, and inter-arrival time sequences achieve 77.1%, 78.1%, and 63.2%
그리고 이들을 통합한 ensemble CNN-RNN는 82.3% accuracy를 확보함.
결국 deep learning architecure을 활용한것 만으로는 machine learning (random forset)모델의 성능 대비 분류성능이 더 좋아지지 못함.
그러나 최종적으로 ranodm forest classifier와 CNN+RNN network의 ensemble 모델로 단순 Random Forest classifier보다 더 좋은 best performance를 확보할 수 있음. ensemble하기 위해서 다음과 같이 CNN-RNN ensemble의 softmax output을 log probability output of the RF classifier와 함께 average한다.
This requires us to average the Softmax output of our CNN-RNN ensemble with the log probability outputs of the Random Forest classifier provided by scikit-learn.
Let σRF (x), σd1 (x), σd2 (x), σd3 (x) be the output probabilities for Random Forest, packet, payload, and inter-arrival time trained classifiers respectively.
The final combined classifier amounts to choosing the SNI class with the highest average output across four total classifiers:
추가 개선 사항
특정 minimum connection threshold 조건으로 저자의 DL model의 최적화 진행을 하면 더 좋은 성능이 확보될 수 도? (e.g. hyperparameter optimization, etc…)
packet, payload, inter-arrival time sequence 각각을 위한 model architecture optimization + 각각 최적의 model로 훈련 후 ensemble하면 더 좋은 결과가 나오지 않을까?
CNN-RNN model들을 ensemble하는 방식을 변화시켜볼 수도 있을것이다. 이 논문의 best result로는 output of each CNN-RNN softmax가 동일하게 weight되었지만, 만약 다르게 weight된다면 다른 결과를 확보할 수 있을것이다.
packet과 payload size가 correlate되어있어서 이 두가지 feature data로 훈련한 CNN-RNN model을 비슷한 signal을 학습하게 됨. 그래서 inter-arrival time classifier에 더 높은 weight을 주는 ensemble 방식이 performance가 더 좋을 수 있다.
반대로 inter arrival time으로 훈련된 classifier의 performance결과가 낮은 경우가 많았기때문에, 이 모델에 주어지는 weight를 줄여서 전체 성능을 더 높일 수도 있을것이다.
directional features
-다음과 같이 packet sequence내의 각 packet의 directionality설정.
- client->server: 1
- server->client:-1
- else(i.e. padding): 0
이 논문에서 확인한 바로는 directionality가 추가되어서 뚜렷한 improvement가 보이지 않는다.
-network flow data에서 informative features를 extract하고 analyze하는 방법 variation
References
Niloofar Bayat, et al. (2021) Deep Learning for Network Traffic Classification