Cost-sensitive Learning
cost-sensitive machine learning은 cost matrix를 사용하는 methods를 일컫는다. cost matrix란 “a matrix that assigns a cost to each cell in the confusion matrix”.
classification model를 평가하는데에 활용되는 confusion matrix의 각 cell(case)에 다음과같이 해당하는 cost (C(x,x) 함수)를 배정하고 model의 cost를 최소화하는 것을 목표로 한다.
| Actual Negative | Actual Positive
Predicted Negative | C(0,0), TN | C(0,1), FN
Predicted Positive | C(1,0), FP | C(1,1), TP
Actual 값과 prediced 값이 다르게 제대로 분류하지 못한 False Positive cost C(1,0)FP와 False Negative cost C(0,1)FN가 cost에 해당된다.
==> Total Cost = C(0,1) * False Negatives + C(1,0) * False Positives
특히, disease diagnosis와 같은 binary classification에서는 False Negative(actual positive인데, negative로 잘못 분류한 경우)의 cost가 훨씬 더 높아야한다.
cost값을 어떻게 설정할지가 매우 중요하다.
effective heuristic 방법으로는 class distribution (observed in the training data)에서 minority vs. majority 비율을 그대로 사용하는 것이다.
예를 들어, minority vs. majority 비율이 1:100 이라면, 다음과 같이 cost를 설정할 수 있다.
| Actual Negative | Actual Positive
Predicted Negative | 0 | 100
Predicted Positive | 1 | 0
이렇게 heuristic을 기반으로 시작하여 cost를 tuning해 나아갈 수 있다.
cost-sensitive resampling
In imbalanced classification, data resampling refers to techniques that transform the training dataset to better balance the class distribution.
undersampling방법들을 통해 majority class에서 sample들을 delete하거나, oversampling 방법들을 통해 minority class sample를 새롭게 synthesize한다.
cost-sensitive목적으로 resampling을 하는 방식은 class distribution을 balance시키는 것이 목적이 아니라, focus is on changing the composition of the training dataset to meet the expectations of the cost matrix.
For imbalanced classification where the cost matrix is defined using the class distribution, then there is no difference in the data resampling technique.
이전 posting에서 다룬 imbalanced dataset의 전처리 방법으로 크게 random resampling과 synthetic sampling를 다루었는데, 이 방법들이 활용된다.
Resampling 방식:
Random resampling : ROS(random over sampling), RUS(random under sampling)
Synthetic sampling : SMOTE, GAN
cost sensitive algorithms
보통 machine learning algorithm은 evenly distributed class들간의 classification을 위해 만들어져 있다. 그러나 현존하는 machine learning algorithm이 cost matrix를 활용하도록 modify할 수 있다.
- algorithm-specific modification (sci-kit learn SVC, DecisionTreeClassifier)
sklearn의 machine learning library를 사용하는 경우에는 decision trees나 support vector machine과 같은 popular algorithm에 customized된 modification방식들을 사용할 수 있다. class_weight argument를 통해서 cost-sensitive extension을 설정할 수 있다.
- using costs as penalty for misclassification (sci-kit learn LogisticRegression, RidgeClassifier)
다른 general 방식은 cost를 penalty로 활용하는 것이다.
Given that most machine learning algorithms are trained to minimize error, cost for misclassification is added to the error or used to weigh the error during the training process.
This approach can be used for iteratively trained algorithms, such as logistic regression and artificial neural networks.
sklearn의 LogisticRegression, RidgeClassifier의 class_weight argument를 통해 설정할 수 있다.
keras library를 통해 DL neural network의 cost-sensitive augmentation도 가능하다. class_weight argument와 fit() 함수를 통해서 모델의 training process동안 cost-sensitive를 설정할 수 있다.
cost-sensitive algorithm은 종종 class-weighted algorithm으로도 불린다. (e.g., “Cost-sensitive Logistic Regression” = “Class-weighted Logistic Regression”)
cost sensitive reweighing
cost sensitive reweighing방법으로:
- 각 클래스별 개수를 반영하여 objective function(cost function)에 가중치를 부여
- 각 클래스별 데이터 개수의 반비례를 가중치로 설정
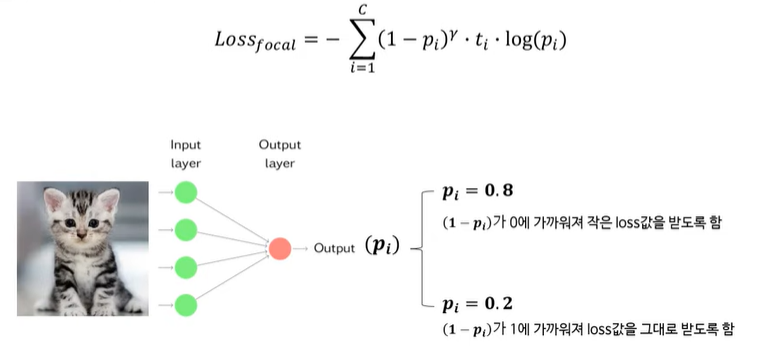
focal loss
맞추기 쉬운 클래스 sample들의 가중치를 줄이고 맞추기 어려운 클래스 sample에 대한 학습에 focus를 맞추는 방식. 가중치를 sample 단위로 부여한다.
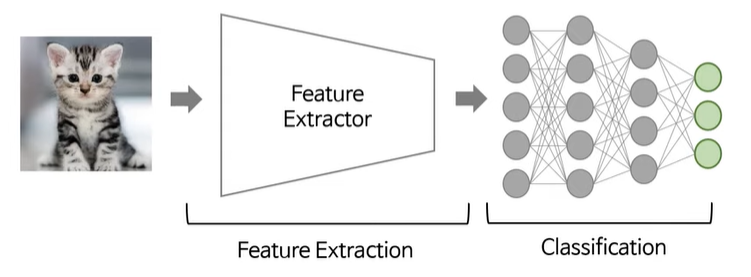
two-stage training
기존에는 end-to-end 방식으로 feature extraction과 classification이 한번에 진행되지만, two-stage training방식에서는 classifier re-training approach를 수행한다. 즉, 먼저 feature extractor와 classifier를 한번에 학습시킨 후, 그 다음 feature extraction부분은 고정하고 classifier 부분만 재학습시킨다.
결국 분류를 위한 경계선이 classifier를 통해 생성되기때문에 classifier를 잘 학습시키는것이 도움이 될 수 있다.
cost-sensitive ensembles
기존의 machine learning model의 prediction들을 filter 또는 combine해서 misclassification cost를 take into account 하도록하는 방법이다.
“wrapper methods”라고도 불린다 as they wrap a standard machine learning classifier. They are also referred to as “meta-learners” or “ensembles” as they learn how to use or combine predictions from other models.
thresholding
use of a machine learning model to predict the probability of class membership, then using a line search on the threshold at which examples are assigned to each crisp class label that minimizes the cost of misclassification.
threshold optimization is used more generally for binary classification tasks, although it can easily be modified to minimize cost instead of a specific type of classification error metric.
meta-cost
bagged ensemble을 사용해서 training data의 example들을 relabel하는 과정을 통해 transformed dataset을 확보하고 이를 훈련에 활용해서 cost를 더 minimize할 수 있는 classifier model을 확보한다.
data preprocessing technique that relabels examples in the training dataset in order to minimize cost.
In MetaCost, first a bagged ensemble of classifiers is fit on the training dataset in order to identify those examples that need to be relabeled, a transformed version of the dataset with relabeled examples is created, then the ensemble is discarded and the transformed dataset is used to train a classifier model.
modification to decision tree ensembles to take the cost matrix into account
Most notably cost-sensitive versions of AdaBoost such as AdaCost.
References
- “[Open DMQA Seminar] Handling imbalanced datasets” by 황하은 [인공지능공학연구소]: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CU2GF0du36o
- “Cost-Sensitive Learning for Imbalanced Classification” by Jason Brownlee : https://machinelearningmastery.com/cost-sensitive-learning-for-imbalanced-classification/
- “How to Develop a Cost-Sensitive Neural Network for Imbalanced Classification” by Jason Brownlee : https://machinelearningmastery.com/cost-sensitive-neural-network-for-imbalanced-classification/