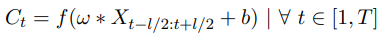CNN for Time Series Classification
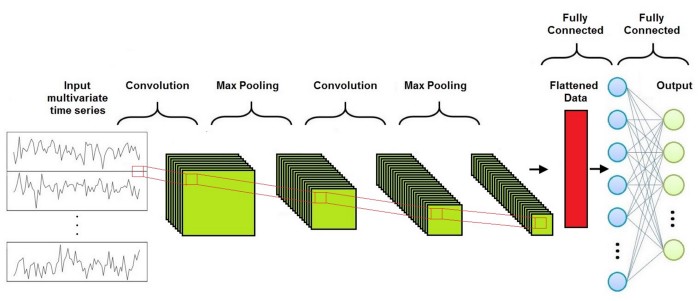
Time series CNN
CNN모델을 통해 분류문제를 해결할 수 있는 time series data는 stock indices, climate measurements, medical tests, 등 매우 다양한다. time series classification을 구현하는 방법은 다양하지만 그 방법이 크게 두개의 stages로 구현된다.
- first stage: 어떤 algorithm을 사용해서 분류하려는 time series의 difference를 측정하거나 또는 활용가능한 statistical tool이나 advanced mathematical methods를 사용해서 time series 데이터를 feature vectors로 변환시킨다.
- second stage: 어떤 algorithm을 사용해서 분류작업을 수행한다. 여기서 사용할 수 있는 algorithm은 k-nearest neighbors이나 SVM 부터 deep neural network model까지 매우 다양한다.
보통 이런 algorithm들을 적용하기 전에 some kind of feature engineering이 classification전에 따로 수행되어야하는 경우가 많다. 그러나 CNN(convolutional neural networks)과 같은 end-to-end deep learning 모델을 사용하면 feature engineering을 framework내에 포함하여 따로 사람이 진행해야하는 단계를 skip할 수 있다. (able to extract features and create informative representations of time series automatically.)
CNN을 통한 time series classification은 큰 장점을 가지고있다고 한다. Highly noise-resistant한 model이기때문에 time independent하고 informative한 deep features를 extract할 수 있다. CNN의 weight sharing과 translation invariant의 장점을 활용할 수 있다.
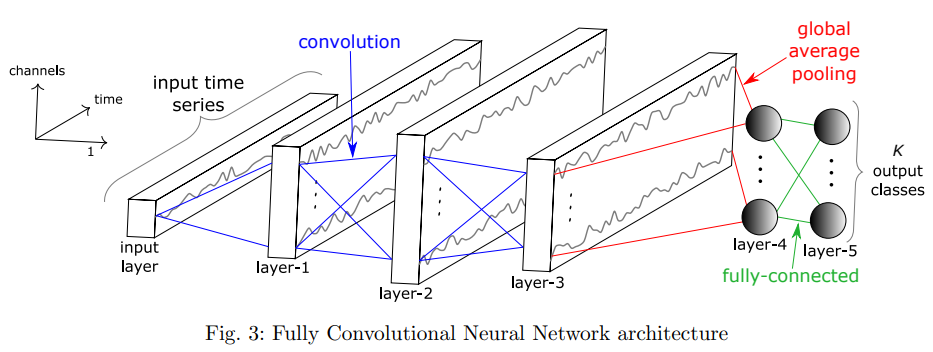
CNN algorithm 기반의 classification model의 전반적인 구조는 다음과 같다:
convolutional layer, pooling layer, fully-connected layer로 형성되어있다. (fully connected layer전에 convolutional과 pooling layer는 필요한 만큼 반복됨.)
Convolutional Layer
convolution operation이 CNN의 핵심 building block이다. Convolution operation은 filter matrix를 적용해서 input series of feature maps에 convolution을 수행하고 different series of feature maps를 output하는 것이다. 이 과정을 통해 high-level features를 추출해내는 것이다.
Review on CNN
지난 posting에서 CNN을 주제로 기본적인 내용이 설명되었음 - CNN(Convolutional Neural Network) 일반적으로 CNN이 많이 활용되는 image classification과 같은 문제에서 구현되는 2D convolution을 기반으로 filter, kernel 그리고 convolution의 parameter들에 대해 조금 더 상세하게 review해본다.
Filters & Kernels
input layer가 여러 channels(보통 이미지의 경우 3개의 channels - R,G,B)로 구성되어 있듯이, filter는 kernel로 구성되어있다. Hierarchical point of view에서는 the concept of layer = concept of filter가 동등 level이고 channel과 kernel은 바로 하위 level에 해당한다. Channels와 feature maps는 동일한것이다.
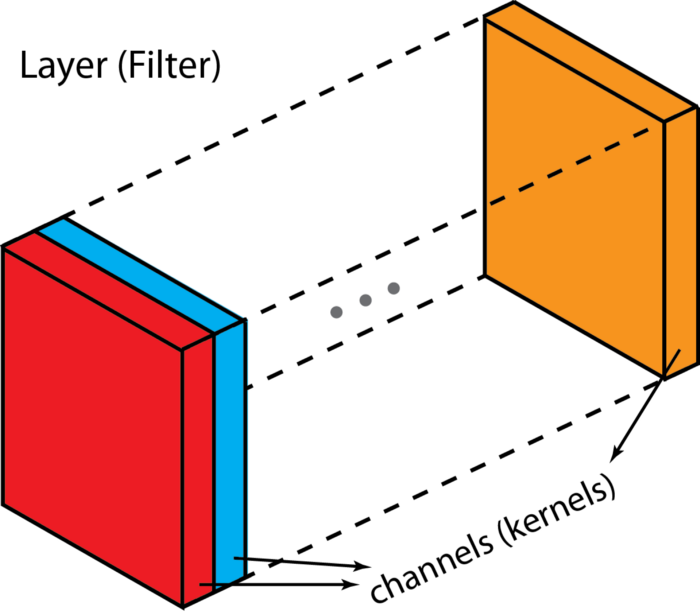
filter과 kernel는 서로 interchangeably 사용되기도 하기때문에 헷갈릴 수 있다. 한다. 정확하게는 kernel은 2D array of weights를 의미한다. filter은 여러개의 kernel들이 stacked된 3D structure를 의미한다.
“filter = collection of kernels”
각각의 kernel은 input channel의 different aspects를 강조하며 unique하다. 그러나 filter가 2D인 경우에는 filter와 kernel이 동일하게 2D array of weights로 볼 수있다. 그냥 “filter”라는 collection에 한개의 kernel만이 있다고 생각하면 된다.
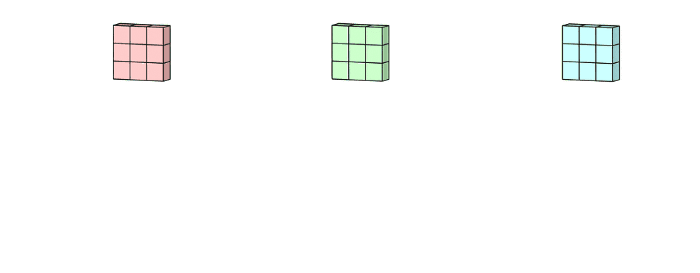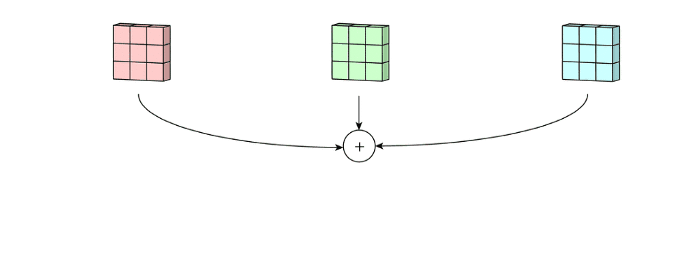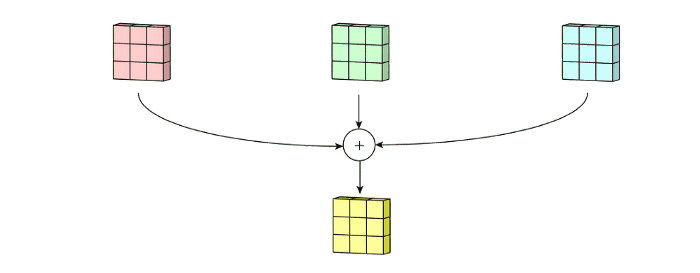
multi-channel convolution을 보면, 각 kernel이 previous layer의 각 input channel에 적용되어서 one output channel을 생성해낸다. 이렇게 kernel-wise process를 모든 kernel에 대해 수행하고 multiple channels를 생성한다. 이 channel들은 summed together되어서 one single output channel을 형성한다. 다음 예시를 통해 그림으로 이 과정을 확인할 수 있다.
예시) input layer of 5 x 5 x 3 matrix with 3 channels에 filter of 3 x 3 x 3 matrix를 적용하면 다음 그림과 같이 convolution이 수행된다. each of the kernels in the filter are applied to three channels in the input layer, separately. 이렇게 3개의 convolution이 수행되고 3 channels with size 3 x 3를 결과로 얻게된다.
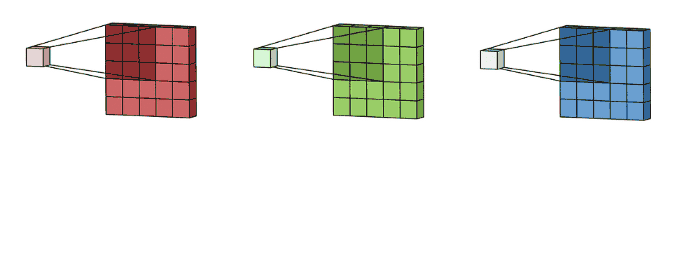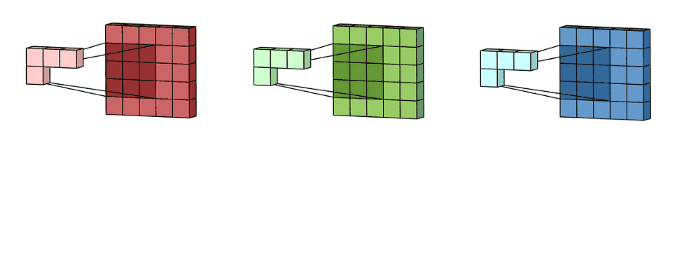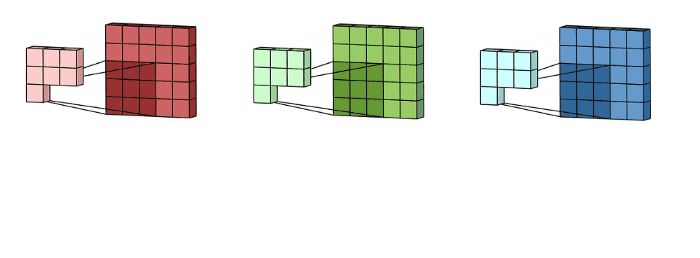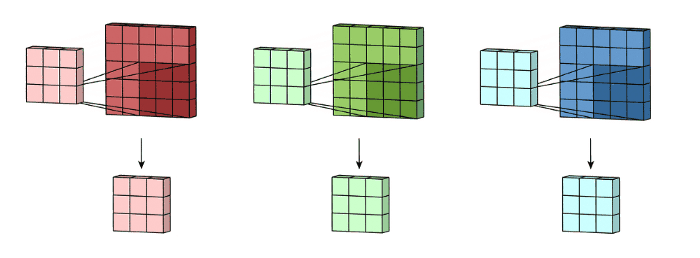
그리고 3개의 channel들이 summed together되어서 (element-wise addition) 하나의 single channel (3 x 3 x 1)을 만든다. 이 channel이 input layer(5 x 5 x 3 matrix)에 filter(3 x 3 x 3 matrix)를 적용한 결과이다.
3D filter matrix를 input layer를 통해 slide한다고 생각해보면 다음 그림과 같이 convolution이 수행된다고 그려볼 수 있다. input layer와 filter는 동일한 depth를 가지고있다는 것이 확인된다. (number of channels = number of kernels)
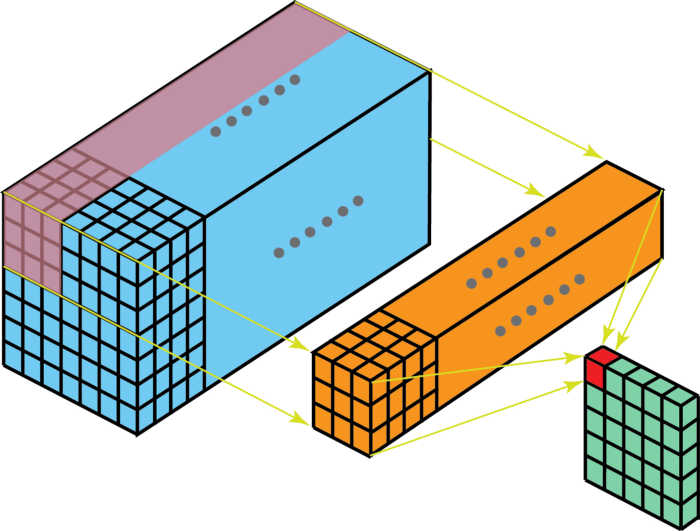
3D filter는 input image의 height & width 이 두가지 방향으로만 움직인다. (그래서 such operation is called 2D convolution) 각각의 sliding position에서 element-wise multiplication과 addition을 수행하고 single number로 결과를 얻는다. 위 그림에서는 filter의 sliding이 5 positions horizontally, 5 positions vertically 움직이며 convolution이 수행된다. 이 과정을 통해 결국엔 single output channel을 얻는다.
input layer가 D_in channels를 가지고있고, output layer가 D_out channels를 가져야한다면, we just need to apply the D-out filters to the input layer. 각 filter는 D_in kernels를 가지고, 각 filter는 one output channel을 output하기때문에, D_out개의 filters를 적용하면, D_out개의 channels를 확보할 수 있다. 이들을 stack해서 원하는 output layer의 형태를 만들 수 있다.
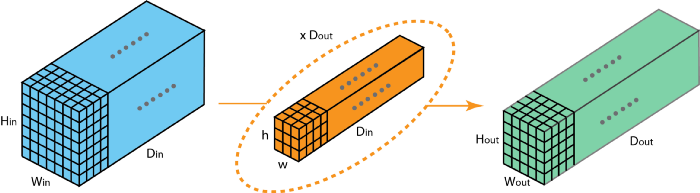
Operation of applying filters
convolution을 통해 input의 different aspects 또는 features를 추출하기위해서 a wide range of different filters가 사용된다. each type of filter helps to extract certain features. (e.g., input image의 horizontal/ vertical/ diagonal edges, etc)
CNN에서는 convolution을 통해 training 과정으로 학습된 weights를 가진 filters를 사용해서 different feature들을 extract한다. 추출된 features를 결국 통합해서 final decision(예측값)을 만들어낸는 것이다.
그래서 convolution은 set of filters로 정의된다. filter가 input feature map의 submatrix에 적용되면 결과는 다음 그림과 같이 sum of product of every element of the filter with the element in the same position of the submatrix이다.
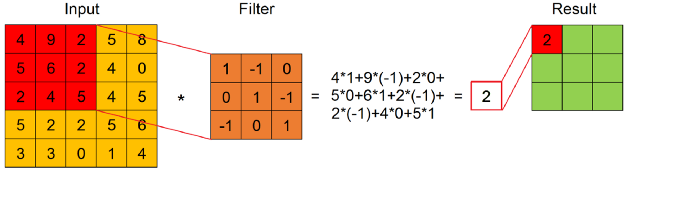
하나의 input feature map과 하나의 filter로 생성되는 convolution result는 ordered feature map (obtained by applying the filter across the width and height of the input feature map)이다.
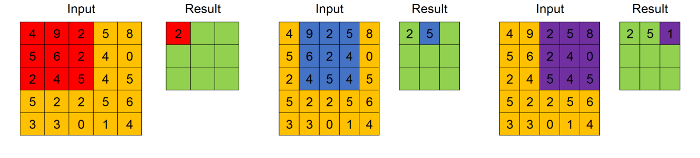
하나의 convolutional layer는 every filter과 every input feature map사이에서 convolution을 수행한다. filters의 value들은 trainable weights이고 훈련과정을 통해서 학습된다.
그외 parameters
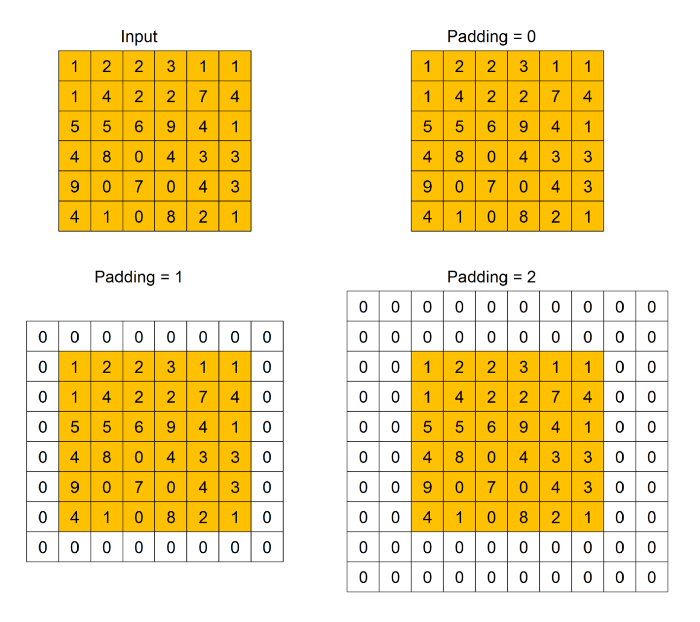
convolutional layer의 주요 parameter는 stride와 padding이다. 그림으로만 간단하게 각각의 parameter를 표현하자면, 다음과 같다.
stride - In particular, the value of stride indicates how many units must be shifted at a time.
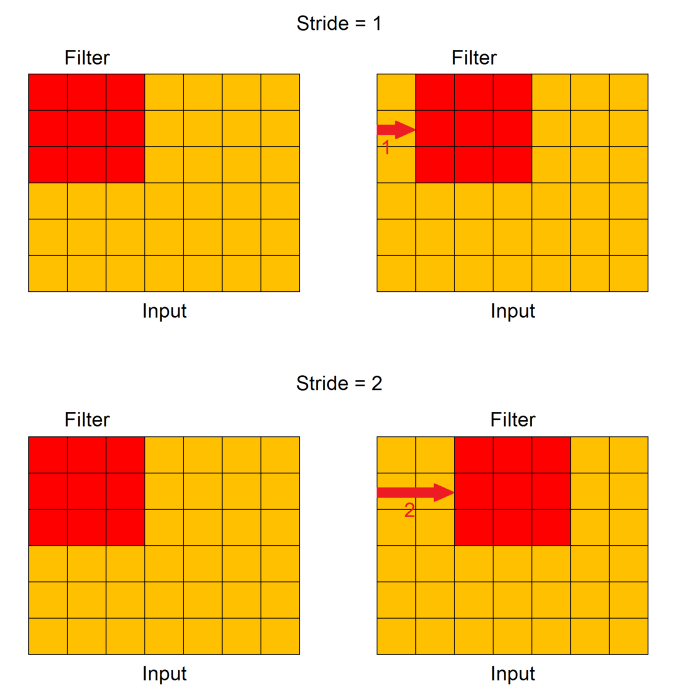
padding - Padding indicates how many extra columns and rows to add outside an input feature map, before applying a convolution filter. 보통 dummy value (=0)로 채워진다. padding이 사용되는 이유는 convolution filter가 input feature map에 적용되면서 size가 감소되기때문에, original size를 preserve하거나 size가 너무 작아지지 않도록 하기 위해서 padding이 활용된다.
1-D Convolution
first stage
1-D convolution 방식에서는 이미지의 height, width에 따라서 두가지 방향으로 filter가 움직이는것이 아니라 time-dimension 한 방향으로만 filter가 움직이며 input feature map에 적용된다.
time series input feature map을 보면 time length=n, width(feature dimension)=k로 설정되있다. (e.g., 하나의 recorded instance가 k개의 variables로 구성되어있고 각각의 variable들이 n개의 time step으로 측정되었음. 시계열 날씨 데이터라면 variable들은 temperature, pressure, humidity, 등이 될 수 있다.)
1-D convolution for time series의 경우에는 다음 그림과 같이 convolution kernels은 항상 time series와 같은 width k를 가지고있지만 length n은 다를 수 있다. 여기서 length n은 kernel_size라는 convolution의 parameter중 하나로 설정될 수 있다.
Given a time series data, kernel이 time series의 beginning에서 부터 end까지 time-dimension 방향으로 convolution을 수행하며 이동한다. (time을 따라 1-D이기때문에 보통 2-D convolution이 images에 적용되는듯이 image의 width와 height에 따라 좌우로 움직이는것이 아님.)
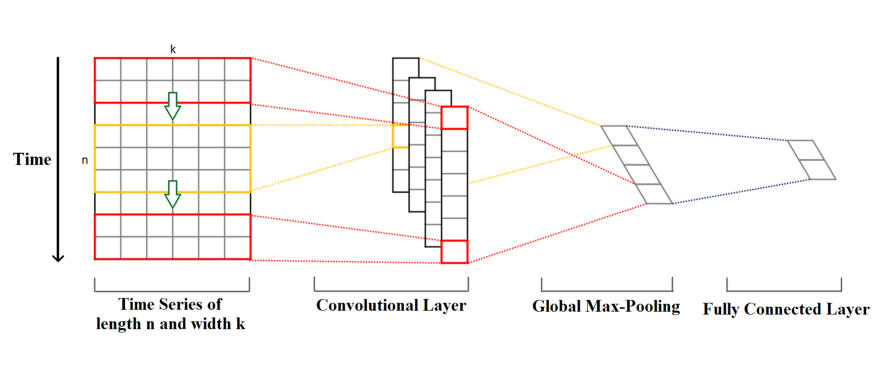
Kernel(filter)의 element들은 특정 given point에서 cover하는 time series data의 corresponding element로 multiply된다. 이 multiplication의 결과들은 더해서 하나의 value로 통합되고, 여기에 nonlinear activation function(ReLU, sigmoid, tanh, 등)이 적용된다.
예시) if convoluting(multiplying) a filter of length=3 with a univariate time series, by setting the filter values = [1/3, 1/3, 1/3], convolution will result in applying a moving average with a sliding window of length=3.
수학적으로 표현하면,
C_t = result of a convolution(dot product) applied on a univariate time series X of length T
w = filter of length l
b = bias parameter
f = final non-linear function (e.g., ReLU)
Resulting value C_t(result of a convolution(one filter) on an input time series X)는 filtering 과정을 통과한 새로운 univariate time series가 된다. 그리고 kernel은 time series data에서 시계열 방향으로 계속 이동하며 다음 value를 생성한다. 그래서 새롭게 “filtered”된 time series의 개수는 convolution kernel의 개수와 동일하다. kernel의 length, different aspects, 그리고 properties에 따라서 initial time series data의 “features”가 “filtered”된 series에 capture되는 것이다. (An intuition behind applying several filters on an input time series would be to learn multiple discriminative features useful for the classification task.)
여기서 kernel을 활용하는 과정은 time series의 generic non-linear transformation (first stage)단계로 볼 수 있다.
Classical MLP와는 다르게, CNN에서는 “weight sharing” property가 활용된다. All time stamps t (within range=[1,T])에 대한 convolution result를 구하기위해서 동일한 filter values w와 b를 가진 convolution이 구해진다. 이 property를 통해서 CNN은 time dimension을 관통하며 변하지 않는 filters를 통해 time series data의 특성을 학습할 수 있다. (매우 중요한 property임!)
Multivariate time series(MTS)를 convolution layer에 input하는 경우에는, filter는 더이상 one dimension이 아닌, input MTS의 dimension과 동일한 dimension을 갖게된다. kernel matrix=[k,n] where k=number of feature dimensions in MTS data, and n=kernel size(length of time step applied to the input feature map)
Filter values w는 targeted dataset에 highly dependent하다. optimal filter values는 classifier가 쉽게 dataset class들을 discriminate할 수 있도록 설정되어야한다. 이런 discriminative filter를 찾기위해서, convolution은 discriminative classifier(second stage)로 follow되어야한다.
discriminative classifying을 수행하기전에 보통 local 또는 global pooling을 각각의 filtered time series vector에 적용한다. 주로 사용되는 max pooling은 각 vector에서 가장 큰 value를 가져가는 것이다. (max외에도 average pooling이 사용되기도 한다.)
Local pooling을 Input time series에 적용하면 time series의 length T를 sliding window구간내에서 aggregate하여 통합한다. 이를 통해서 maximum values로 구성된 새로운 vector가 생성된다.
예시) if sliding window’s length=3, resulting pooled time series have length=T/3. (only if stride=sliding window’s length)
Global pooling을 적용하면, time series가 whole time dimension구간내에서 하나의 real value로 통합된다. 만약 sliding window의 length가 input time series의 length와 동일할 때에 local pooling을 적용하면 동일한 결과가 확인될것이다.
일반적으로 model의 parameter 개수를 drastically 감소시켜서 overfitting 위험을 감소시키는 목적으로 local보다는 global aggregation을 사용한다고 한다.
pooling layer외에도 normalization layer과 같은 deep learning architecture를 함께 사용해서 network이 보다 빠르게 converge할 수 있도록 한다. time series data를 위해서는 batch normalization을 each channel에 대해 수행해서 internal covariate shift across one mini-batch training of time series를 방지한다.
second stage
그 다음, input time series의 representation인 vector가 final feature vector로 regular fully connected layer(final discriminative layer)에 input되어서 분류하려는 class variables에 대한 probability distribution를 구하고 가장 높은 확률을 가진 class variable을 예측 class로 결정한다. 보통 이 layer에서는 softmax operation이 활용된다. 종종 final softmax layer전에 additional non-linear FC layer가 활용되기도 한다. 여기에서는 기존 MLP와 동일하게 feed-forward pass와 backpropagation이 순차적으로 진행된다.
CNN architecture for TSC(Time-Series Classification):
Hyperparameters
다음 hyperparameter들을 조정하여 CNN의 성능을 tuning할 수 있다.
number of convolution filters
number of times the input is processed/interpreted.
convolution filter size(kernel size) and initial values
kernel size는 number of time steps (considered in each “read” of the input sequence)를 제어함.
더 큰 kernel size –> less rigorous reading of the data를 얻게되지만, more generalized snapshot of the input이 확보 가능하기도 함.
pooling method and size
보통 max pooling, avg pooling이 사용 됨.
weight initialization
activation function
number of epochs
data preparation (e.g., normalization, standardization)
regularization (e.g., dropout rate)
References
- [blog] how to use convolutional neural network for time series classification: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-use-convolutional-neural-networks-for-time-series-classification-56b1b0a07a57
- [blog] Time Series Classification with Deep Learning by Marco Del Pra https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-classification-with-deep-learning-d238f0147d6f
- [blog] A Comprehensive Introduction to Different Types of Convolutions in Deep Learning by Kunlun Bai https://medium.com/towards-data-science/a-comprehensive-introduction-to-different-types-of-convolutions-in-deep-learning-669281e58215
- [paper] multi-scale convolutional neural network: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.06995.pdf
- [paper] Deep learning for time series classification: a review(2019, Hassan I.F., et al)